Alright, picture this: You’re making your morning coffee, right? You boil the water in the kettle, it steams away, and then... that steam just vanishes into thin air. Poof! Gone. Or maybe you’re baking a delicious batch of cookies – yum! – and your oven is humming along, generating all this heat, but then you open the door, and a huge gust of that expensive, hard-won warmth just escapes into your kitchen. Ever feel like there’s a bit of a missed opportunity there?
You probably do! Because, let’s be honest, we all instinctively hate waste. We try to use all the leftovers, we recycle, we turn off lights. So, what if I told you that for decades, our big, fancy power plants have been doing something pretty similar to that vanishing kettle steam, but on a colossal, industrial scale?
The Great Energy Escape: Traditional Power Plants
Most traditional power plants work by burning fuel (natural gas, coal, etc.) to heat water, create steam, and spin a turbine to generate electricity. This is great for getting power to your home, obviously. But here's the kicker: after that steam has done its job, a huge chunk of its remaining heat energy is just... expelled. Vented into cooling towers, dissipated into the atmosphere, or sent into rivers. It’s like buying a two-scoop ice cream, eating one, and throwing the other scoop away. Ouch.
This wasted heat can account for as much as two-thirds of the original energy content of the fuel! Think about that for a second. We're talking about massive amounts of energy, literally just evaporating. Crazy, right?
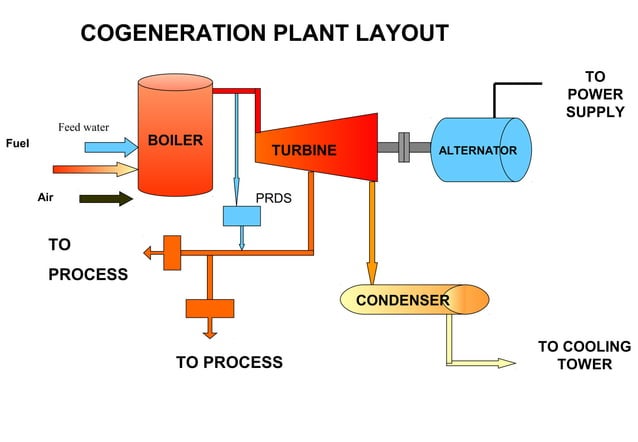
Enter the Hero: What Is a Cogen Power Plant?
This is where the super-smart engineers come in, scratching their heads and thinking, "There has to be a better way!" And they found it. It’s called a Cogeneration Plant, or Cogen for short. You might also hear it called CHP, which stands for Combined Heat and Power. Sounds fancy, but the idea is actually wonderfully simple.
Imagine if, after your coffee kettle steamed, you could immediately capture that hot steam and run a mini-turbine to power a light bulb, and then use the remaining heat to warm your mug. That’s essentially what Cogen does, just on a much bigger, more sophisticated scale.
How Does This Magic Happen?
Instead of letting all that post-electricity-generation heat float away into the ether, a Cogen plant captures it. It uses that heat for something else useful. So, from a single fuel source (like natural gas), it generates two forms of energy:
- Electricity (to power lights, computers, factories, you name it)
- Useful Thermal Energy (aka, heat!)
This useful thermal energy can be in the form of steam, hot water, or even hot air. And it's not just "kinda warm"; it’s hot enough to actually do things. Like, really important things!
Why Should We Care? (Beyond the Cool Factor)
The benefits of Cogen are huge, and they touch on some really important issues:
-
Efficiency, Baby!
This is the big one. Traditional power plants are typically around 35-50% efficient in converting fuel into electricity. Cogen plants, by utilizing that "waste" heat, can achieve overall efficiencies of 70-90%. Think about that for a second! That’s a massive leap. It means we're getting way more bang for our buck from the fuel we burn.
-
Lower Energy Costs:
More efficiency means less fuel needed to produce the same amount of useful energy. This translates directly to lower operating costs for the businesses and institutions that use Cogen. Who doesn't love saving money?
-
Reduced Environmental Impact:
Burning less fuel means fewer greenhouse gas emissions. Cogen plants are a really important tool in reducing our carbon footprint and combating climate change. It's a win for the planet, and for our lungs!
-
Reliability and Resilience:
Many Cogen plants operate on-site at facilities (like hospitals or universities). This means they have their own power source, which can be critical during grid outages or extreme weather events. If the main power grid goes down, they can keep the lights (and heat!) on. Pretty neat, huh?
Where Do We See Them?
You might not realize it, but Cogen plants are already hard at work all around us. They’re particularly popular in places that have a constant need for both electricity AND heat or cooling. Think about:
- Hospitals: They need electricity, hot water for sterilization, and heating/cooling.
- Universities and Campuses: Dorms, labs, lecture halls – all need power, heat, and sometimes chilled water for air conditioning (you can use waste heat to power absorption chillers!).
- Industrial Facilities and Factories: Many manufacturing processes require massive amounts of steam or hot water.
- Data Centers: Need a ton of electricity and have significant cooling needs.
- District Heating Systems: Some cities use Cogen to provide heat to entire neighborhoods.
So, the next time you see steam rising from a factory or a large building, don't just think "waste." You might actually be looking at a sophisticated Cogen system, busy saving energy, cutting costs, and doing its bit for a greener future. It's truly the ultimate energy multitasker, and frankly, we need more of them!