Ever just kick back on the couch, remote in hand, and think, "Hey, how much electricity is this giant glowing rectangle actually sucking down?" No? Just me? Well, stick around, because it’s actually a pretty cool little rabbit hole to tumble down! We're talking about the humble watt, the invisible force behind your binge-watching sessions.
For most of us, electricity is just... there. We plug things in, they work. But understanding even a little bit about how much power our gadgets use can be super interesting and surprisingly empowering. Let's pull back the curtain on your TV's energy habits!
The Big Question: How Many Watts Does a TV Gobble Up?
Alright, let’s get straight to it. If you’re imagining your TV is a greedy monster guzzling electricity like it’s going out of style, prepare for a pleasant surprise! Modern TVs are actually pretty efficient. We’re not in the era of those old, bulky tube TVs anymore, which could truly chug power.
The answer isn't a single, neat number because it depends. A lot. Think of it like asking, "How much fuel does a car use?" Well, is it a compact sedan or a monster truck? Is it idling or speeding down the highway? TVs are similar!
What Makes a TV Thirsty (or Not)?
There are a few key players that determine your TV’s wattage, and knowing them is half the fun!
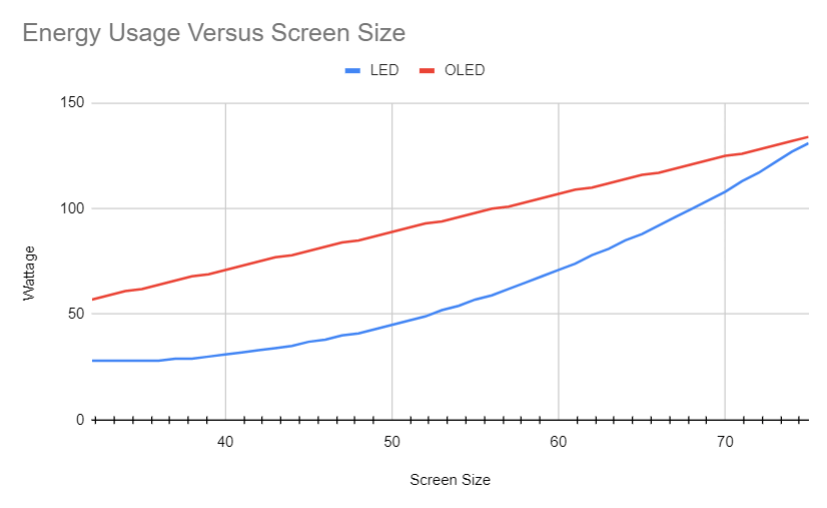
Screen Size: Bigger Usually Means More Juice
This one’s pretty intuitive, right? A bigger screen has more pixels to light up, so it generally needs more power. A smaller 32-inch TV might only use around 20-40 watts, which is less than a traditional incandescent light bulb! Move up to a common 55-inch model, and you’re probably looking at something in the range of 60-100 watts. And those massive 75-inch-plus screens? They can climb to 150-200 watts or more. Still, not *insane*, right?
Screen Technology: LED, OLED, QLED – What's the Diff?
This is where things get really fascinating!
- LED TVs (and LCD with LED backlighting): These are super common and generally quite energy-efficient. They use LEDs to light up the screen. Most modern TVs fall into this category.
- OLED TVs: Ah, the fancy ones! OLED pixels generate their own light. This means when a pixel needs to be black, it simply turns off. How cool is that? This can actually make OLED TVs quite power-efficient for darker scenes (like a space movie) because parts of the screen are literally using zero power. But for really bright, white scenes, they can sometimes use a bit more than an equivalent LED.
- QLED TVs: These are essentially souped-up LED TVs with quantum dots to enhance color and brightness. They're also generally efficient, often comparable to good LED models.
Brightness Settings and Content: The Secret Power Savers
Here’s a simple one: the brighter your TV is set, the more power it uses. Cranking it up to max brightness might look dazzling, but it's like revving your car's engine – more effort, more fuel. Many TVs have "eco modes" or "power-saving settings" that automatically adjust brightness based on ambient light. Using these can save a surprising amount of energy over time without you even noticing a difference in picture quality.
Also, what you’re watching matters! A brightly lit cartoon uses more power than a dark, moody drama (especially on an OLED TV where dark pixels switch off!).
Putting Watts into Perspective: Fun Comparisons!
Okay, so 60-100 watts for a common TV sounds like... a number. But what does that *mean*?
- A Regular Light Bulb (old school): A traditional incandescent bulb used to be 60-100 watts. So, your 55-inch TV uses about the same power as one old light bulb! If you compare it to a modern LED bulb (which might be 8-10 watts), your TV uses more, but still not crazy amounts.
- A Hair Dryer: Try 1500-2000 watts. Your TV is a gentle breeze compared to that!
- A Microwave Oven: Heating up your leftovers often requires 1000-1500 watts.
- A Gaming PC: A powerful gaming rig can pull 300-600 watts, especially when running a demanding game. Your TV is much more chill.
See? Suddenly, your TV isn't looking like such an energy hog, is it? It's pretty amazing how much visual magic we get for so little power.
The Standby Myth: Does Your TV Sip Power When Off?
Yes, a little. When your TV is "off" but not unplugged, it's usually in a low-power standby mode, waiting for your remote control signal. This typically consumes a tiny amount of power, often less than 1 watt. It's like leaving a tiny night light on. Over a year, this can add up to a few dollars, but it’s really not a major drain for most people. If you're super diligent or going on a long vacation, unplugging can save those few pennies!
Why Does Any of This Matter?
Beyond just satisfying a random spark of curiosity, understanding how much power our devices use helps us appreciate the technology, make smarter choices (especially when buying new electronics – look for Energy Star ratings!), and even be a tiny bit more mindful of our energy footprint.
So, next time you're deep into a documentary or lost in a gripping series, you can smile, knowing that your entertainment hub is actually quite the efficient little marvel. Pretty neat, right?