Ever had that moment when your phone battery dies right when you're about to show your friend that perfect meme? Or when the internet cuts out mid-binge and you're left staring into the digital abyss? Yeah, me too. It’s a harsh reminder of just how much we rely on that invisible force zipping through the wires to our devices. But have you ever paused to think, where does all that juice actually come from?
For a surprisingly long time, and still in many places today, a big chunk of it comes from something decidedly un-futuristic: rocks. Black, dusty, incredibly energetic rocks we call coal. I know, I know, it sounds a bit… primal, especially when we’re talking about powering our sleek smart devices. But trust me, there’s a whole lot of clever engineering that turns ancient plants into modern electricity.
The Grand Tour: From Rock to Spark
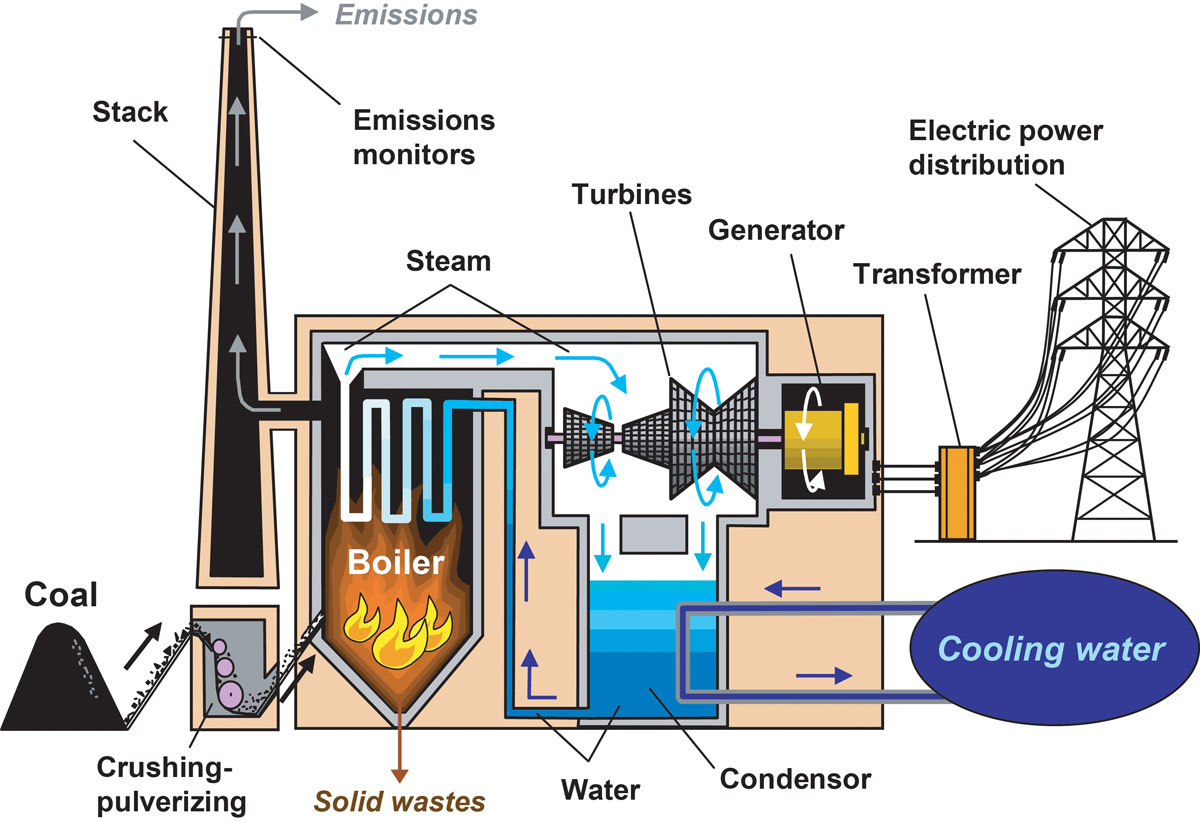
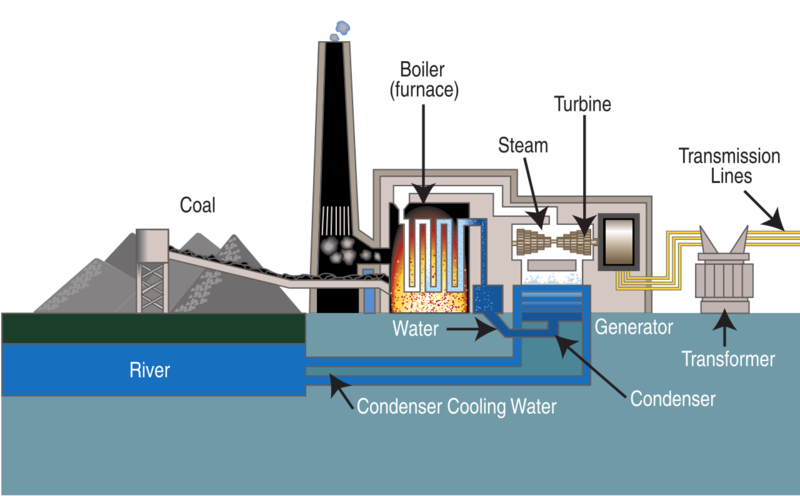
So, how does this magic happen? It all starts, predictably, with the coal itself. Once it's dug out of the earth (often in massive mines, which is a whole other story), it begins its journey. Usually, it's transported by trains, barges, or trucks to a coal-fired power plant. These aren't exactly pretty places, but they are humming with purpose.
First up, once the coal arrives, it doesn't get tossed into a fire pit like some medieval barbecue. Oh no. It's usually crushed into a super-fine powder, almost like flour. This isn't just for kicks; making it powdery means it burns much more efficiently. Think of it like kindling versus a big log – the small stuff catches fire way faster and more completely. This process is called pulverization, if you want to get fancy.
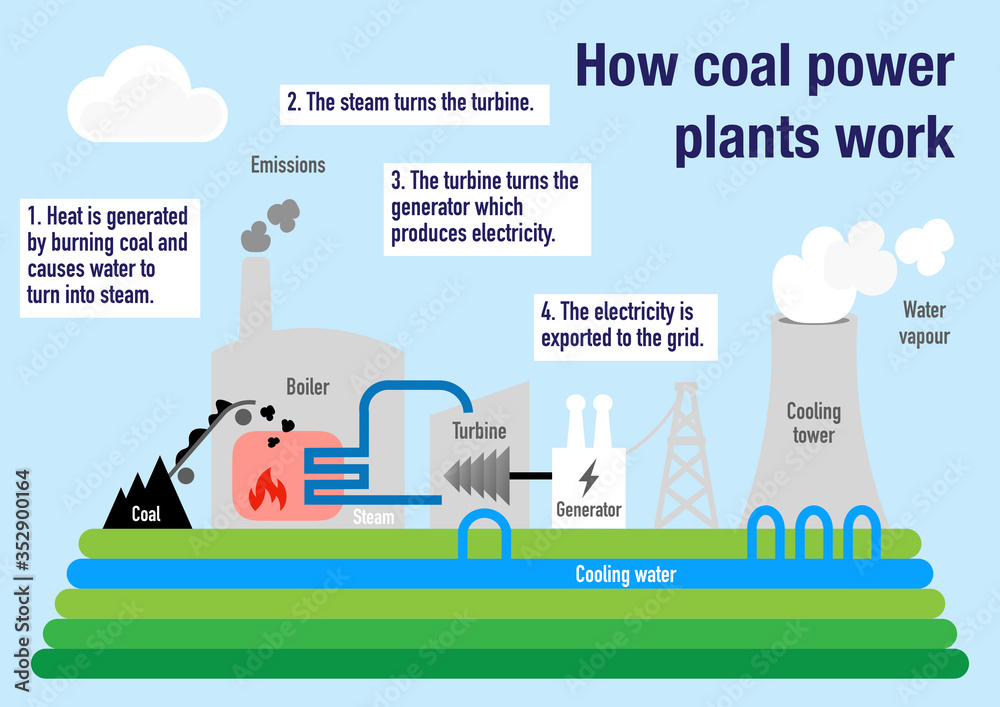
Now, this coal dust is blown into a massive furnace or boiler. Here, it burns at incredibly high temperatures. This intense heat isn’t for show, though. Its job is to boil water. And when I say boil, I mean it turns that water into superheated steam. We're talking pressures and temperatures that would make your kettle blush!
This high-pressure steam is the real workhorse here. It's directed at a series of giant fan-like blades called turbines. Imagine a pinwheel, but instead of wind, it’s being spun by immensely powerful steam. As the steam pushes against the blades, the turbines start to rotate, really, really fast.
And what are these spinning turbines connected to? You guessed it (or maybe you didn't, it's okay!): generators. These are essentially big magnets spinning within coils of wire. When a magnet moves past a coil of wire, it creates an electric current. Ta-da! Electricity is born! (See? Told ya it wasn't rocket science, just *really* hot water and some spinning bits!)
Finally, this newly generated electricity is sent through transformers to boost its voltage, allowing it to travel efficiently across vast distances via power lines, eventually making its way to your home, your phone charger, and your perfectly chilled beverages. And that, my friend, is how a hunk of ancient rock becomes the juice for your Netflix binge. Pretty wild, huh?
Why Bother with Black Rocks?
You might be thinking, "Why coal? In this day and age?" Well, historically speaking, coal was a game-changer. It's relatively abundant in many parts of the world, making it a reliable source. Plus, it has incredible energy density – a small amount of coal holds a lot of potential energy. It was, and in some developing nations still is, an affordable and readily available fuel source to power industrialization and bring electricity to millions.
The Not-So-Pretty Side of Power
Of course, like all good things (especially those involving burning stuff), there's a flip side. Burning coal, while incredibly effective at making steam, also releases a bunch of stuff we'd rather not have in our atmosphere. The biggie is carbon dioxide (CO2), a major contributor to global warming and those pesky greenhouse gases everyone talks about.
Beyond CO2, there are other pollutants like sulfur dioxide (hello, acid rain!), nitrogen oxides (smog!), and tiny particulate matter that can mess with our lungs. So, while coal has powered our progress for centuries, it comes with a pretty heavy environmental price tag. It's sort of our industrial revolution's dirty secret, if you will.
Where Are We Now?
Given its environmental impact, many countries (like mine, and maybe yours!) are actively trying to reduce or completely phase out coal-fired power plants. The focus is shifting dramatically towards renewable energy sources like solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal – which are, let's be honest, much cooler and cleaner. But despite this global push, coal still plays a significant role in the energy mix of many nations, particularly those with rapidly growing economies and abundant domestic coal reserves.
So, the next time your lights flicker on or your laptop charges up, maybe spare a thought for that humble lump of coal. It's a fossil fuel with a fascinating, powerful, and admittedly problematic past, but one that has undeniably shaped the modern, electric world we live in. It's a complex legacy, isn't it?