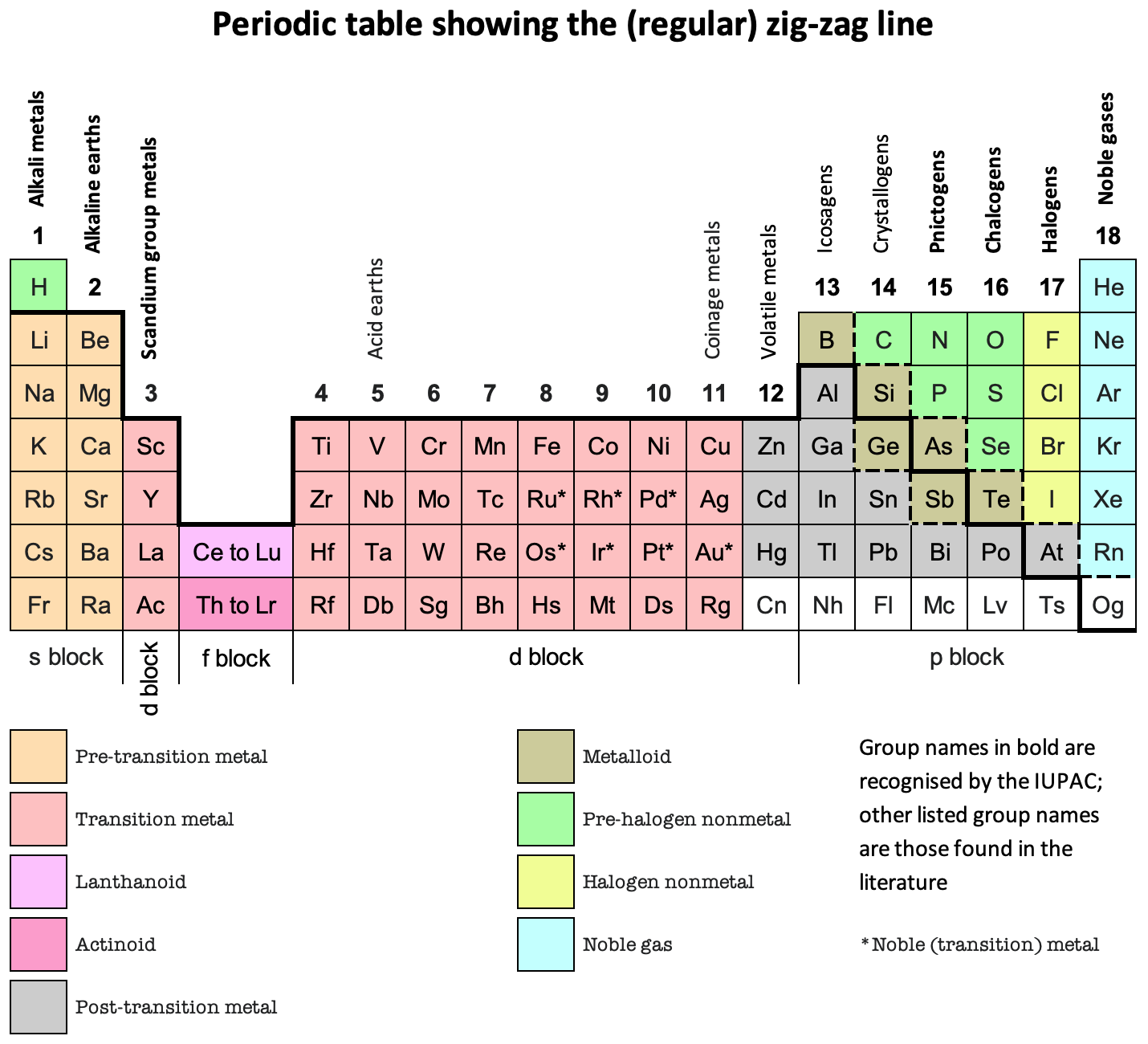
Okay, quick story time. Remember high school chemistry? Yeah, the one where you spent more time trying to balance equations than actually, you know, understanding what was going on? Well, I distinctly remember staring at the periodic table, feeling like I was looking at some alien hieroglyphic system. But there was one thing that always caught my eye: that weird, kinda jagged line snaking its way down the right side. I always wondered, "What's *that* about?!" Turns out, it's pretty important.
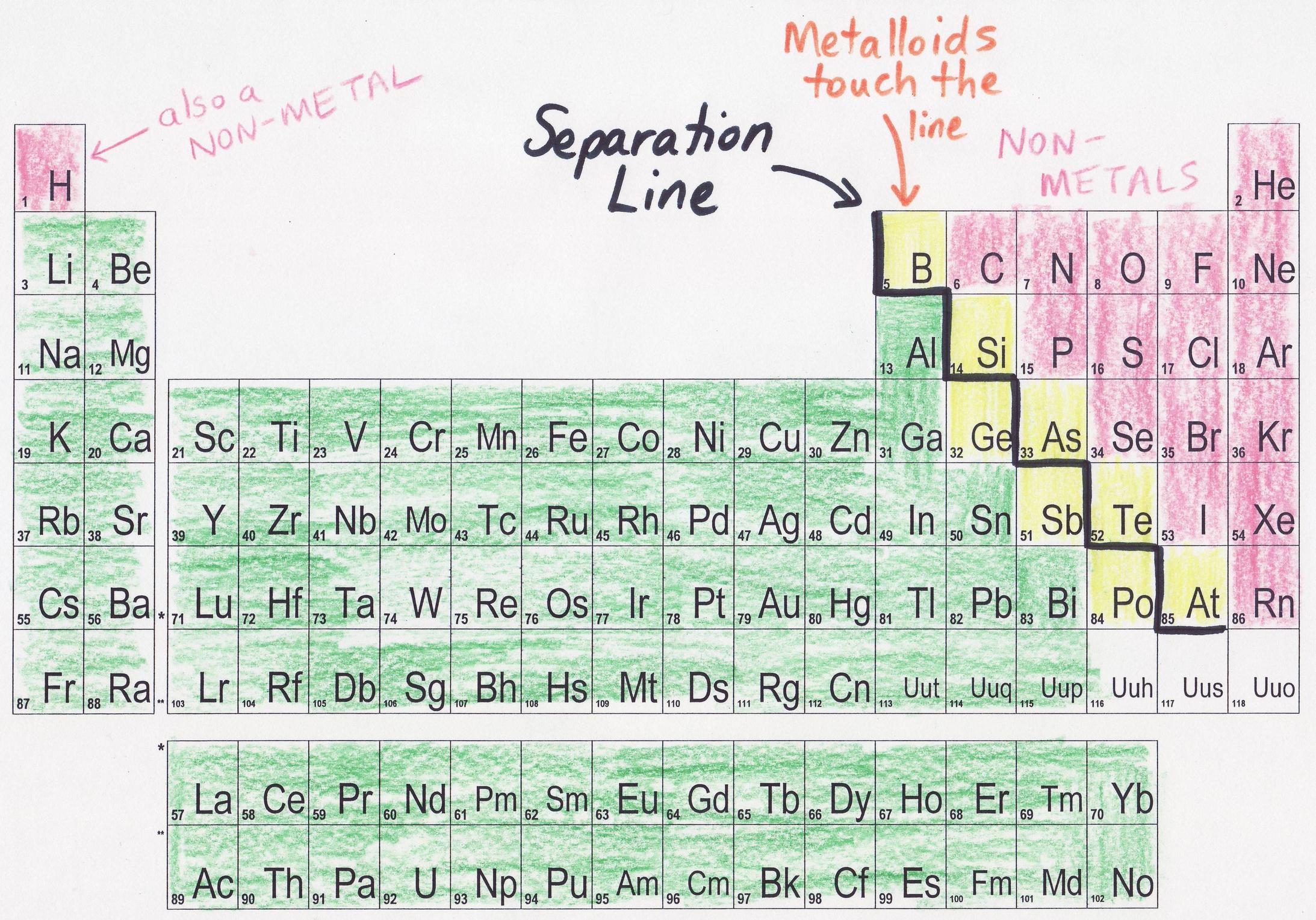
That jagged line? It's not just a random doodle by some bored chemist. It's a visual divider. A subtle, yet significant boundary that separates the metals from the nonmetals. Pretty cool, huh? (And honestly, a little anticlimactic after all those years of wondering.)
Metals vs. Nonmetals: The Great Divide
So, what's the big deal about metals and nonmetals? Well, they're fundamentally different in their properties. Think of it like this: metals are usually shiny, conduct electricity and heat well, and are generally pretty bendable (or malleable, as the textbooks like to say). Nonmetals, on the other hand, are often dull, poor conductors, and tend to be brittle.
That zigzag line essentially acts as a border patrol, keeping these two very different "countries" of elements somewhat separated. But, like any good border, there are a few elements that like to hang out right on the edge, causing a bit of confusion. Which brings us to...
Metalloids: The In-Betweeners
Ah, the metalloids! Also known as semi-metals. These guys are the rebellious teenagers of the periodic table. They don't quite fit in with the metals, and they don't quite fit in with the nonmetals. They possess properties of both, making them incredibly useful and, dare I say, interesting. (Okay, maybe "interesting" is a bit of a stretch for chemistry. But still!)
These elements – like boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te), and polonium (Po) – touch the zigzag line. This isn't a coincidence! They are, by their very nature, transitional elements. They're like the diplomats between the metal and nonmetal nations.
Think of silicon, for example. It's a semiconductor, meaning it conducts electricity under certain conditions but not others. This is *crucial* for making computer chips. Without metalloids, your phone, your laptop, and pretty much every other electronic device you own wouldn't exist. So, yeah, they're pretty important.
Why the Zigzag? Why Not Just a Straight Line?
Good question! (I'm imagining you asked that. Even if you didn't, it's a valid point.) The zigzag shape isn't just for aesthetic value (although, let's be honest, it does add a certain je ne sais quoi to the periodic table). It's there because the transition from metallic to nonmetallic properties isn't abrupt. It's gradual. The jagged line visually represents this gradual change.
If it were a straight line, it would imply a more definitive separation, which isn't accurate. The zigzag acknowledges the existence of the metalloids and the fact that elements closer to the line exhibit properties that are somewhere in between.
So, next time you glance at the periodic table, remember that zigzag line. It's more than just a drawing; it's a key to understanding the fundamental differences between metals and nonmetals, and the fascinating world of the metalloids. It's a visual reminder that even in the seemingly rigid world of chemistry, there's always room for ambiguity and in-betweeners.
And hey, maybe you'll even impress your friends at your next trivia night! (Or, at the very least, you'll have something to think about instead of balancing equations. Just kidding... mostly.)



.PNG)