Let’s talk about energy. Not the frantic, pre-coffee kind, but the literal power that keeps our lights on, our phones charged, and our lives running smoothly. Today's spotlight shines on hydropower, a renewable energy source that’s been harnessed for centuries. But what *kind* of energy is it, exactly? Buckle up; it's a bit more fascinating than you might think!
The Gist: Kinetic to Electric
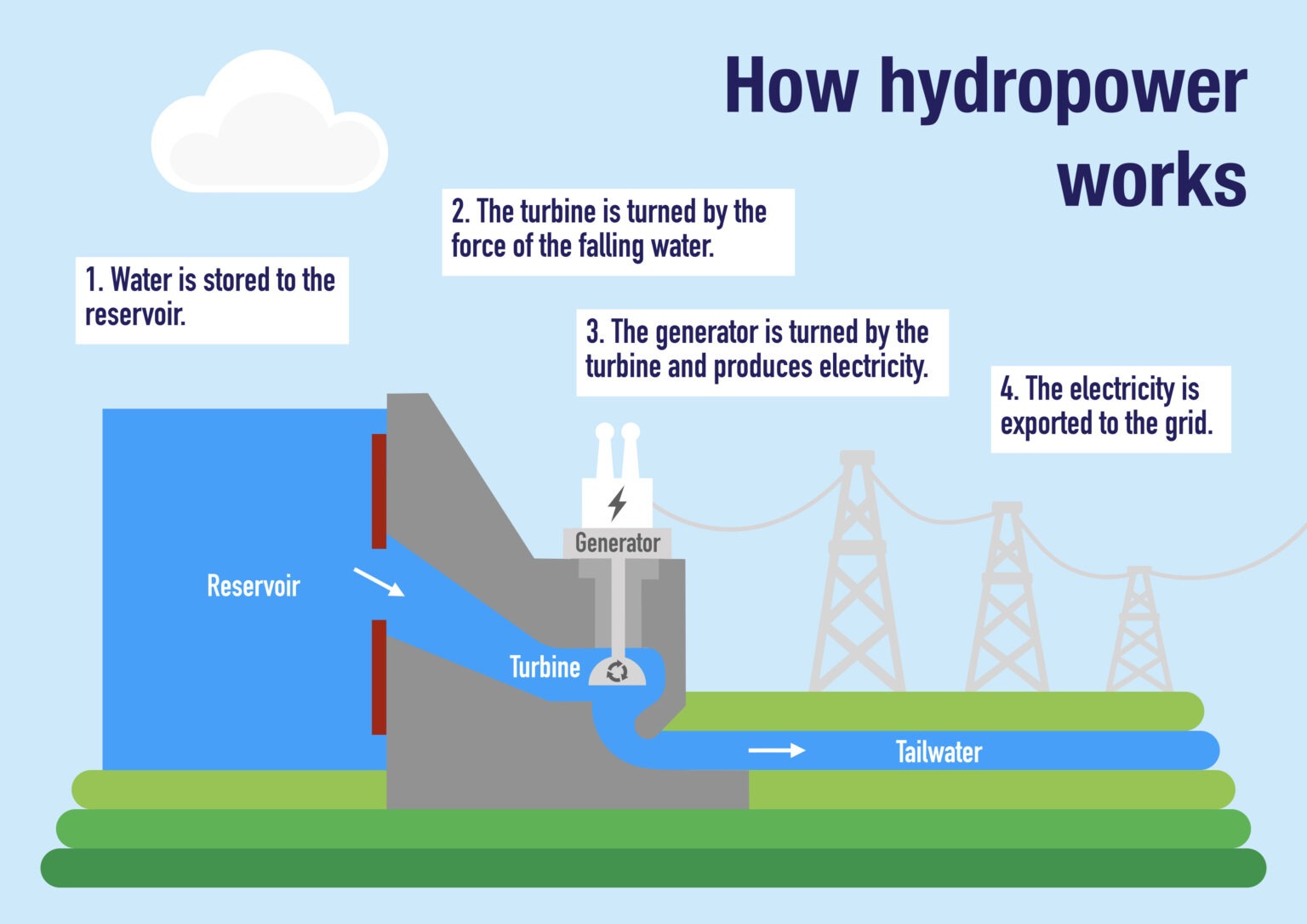
At its core, hydropower is all about transforming kinetic energy – the energy of motion – into electrical energy. Think of it like this: you're on a swing, pumping your legs to gain momentum. That's kinetic energy. Now, imagine that swinging motion being captured and converted into electricity. That's basically what a hydroelectric dam does.
Water stored behind a dam has potential energy due to its height. When released, this potential energy converts to kinetic energy as the water rushes downwards. This rushing water spins the blades of a turbine, which is connected to a generator. The generator then converts the turbine's rotational motion into electricity. Voila! Power from water.
More Than Just Dams: A Diverse Energy Source
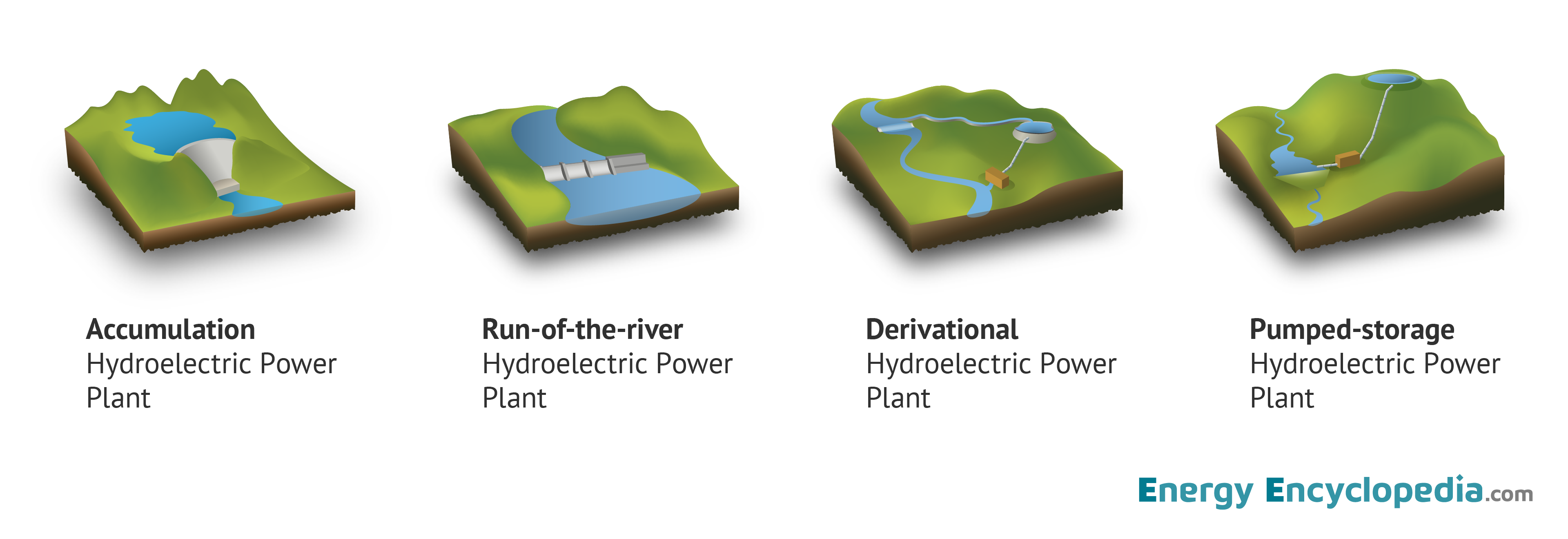
While large dams are the most recognizable face of hydropower, it’s not the only form. Here’s a quick rundown:
- Impoundment Facilities (Dams): The classic. Large reservoirs store water, creating a significant height difference to generate power.
- Run-of-River Hydropower: These facilities utilize the natural flow of a river without creating a large reservoir. They tend to have a smaller environmental impact. Think of it as tapping into the river's natural energy without disrupting its flow too much.
- Pumped Storage Hydropower: This acts like a giant battery. During periods of low electricity demand, water is pumped from a lower reservoir to a higher reservoir. When demand increases, this stored water is released to generate power. It's a clever way to store energy for later use.
Hydropower: Friend or Foe? Weighing the Pros and Cons
Like any energy source, hydropower isn’t without its complexities. It offers several advantages:
- Renewable: Water is a constantly replenishing resource (thanks, water cycle!).
- Reliable: Unlike solar and wind, hydropower can generate electricity consistently, regardless of weather conditions.
- Clean: Hydropower plants produce no direct emissions during operation.
However, it also has its drawbacks:
- Environmental Impact: Dams can alter river ecosystems, affecting fish populations and water quality.
- Displacement: Building large dams can sometimes require relocating communities.
- High Initial Costs: Constructing hydropower facilities requires significant investment.
Cultural Connections and Fun Facts
Did you know that hydropower dates back to ancient times? Water wheels were used for grinding grain and powering machinery long before the invention of electricity. The Romans were masters of aqueducts and water management, demonstrating an early understanding of water's power.
In popular culture, dams often symbolize power and control. Think of the Hoover Dam in countless movies – a monumental feat of engineering and a symbol of human ingenuity.
Fun Fact: The world’s largest hydroelectric power plant is the Three Gorges Dam in China. Its sheer size and power generation capacity are mind-boggling.
Making Hydropower More Sustainable
Thankfully, there’s a growing focus on making hydropower more sustainable. This includes:
- Developing fish-friendly turbine designs.
- Implementing environmental flow regulations to ensure rivers maintain healthy ecosystems.
- Investing in run-of-river hydropower to minimize environmental impact.
From the Dam to Your Desk: A Daily Reflection
The next time you flick on a light switch, take a moment to consider the energy source powering your life. Whether it’s hydropower, solar, wind, or something else, understanding where our energy comes from is a crucial step towards a more sustainable future. Hydropower, with its blend of ancient roots and modern applications, offers a powerful reminder of the ingenuity and responsibility that come with harnessing the earth's resources. Every small choice we make - turning off lights, conserving water - ripples outwards, contributing to a more conscious and sustainable world.