Ever wonder what makes some materials bounce back after you bend them, while others just... well, bend? There's a secret weapon hiding in the world of materials science that explains it all. It's called the modulus of resilience, and trust me, it's way more exciting than it sounds!
Think of it like this: imagine you're stretching a rubber band. You pull it, and it stretches. Let go, and *poof*, it snaps right back to its original shape. That's resilience in action! Now, imagine trying to stretch a piece of clay. You pull it, and… it stays stretched. No bounce-back there. That's where the modulus of resilience helps us understand the difference.
So, What's the Big Deal?
The modulus of resilience is basically a material's superpower. It tells us how much energy a material can absorb *while* staying elastic. Elastic means it returns to its original shape after being deformed. Think of a tiny trampoline inside the material, soaking up all the pressure and then releasing it without getting permanently warped. It's like a material's ability to say, "Bring it on! I can handle the stress and still be me!"
Why is this entertaining? Because it allows us to predict how materials will behave under pressure. If we are designing a car suspension, we need to know that it can absorb impact without permanently deforming. Same goes for airplane wings, bridges, and even the soles of your shoes! Without understanding the modulus of resilience, engineers would be building structures that crumble at the slightest touch. Talk about a nail-biting commute!
Think of it Like a Spring!
A good analogy is a spring. When you compress a spring, it stores energy. When you release it, that energy is released, and the spring returns to its original length. The modulus of resilience is related to how stiff the spring is and how much it can be compressed before it stays compressed.
Materials with a high modulus of resilience are like super-powered springs! They can absorb a lot of energy and bounce back perfectly every time. This is why they're used in things like springs in car suspensions or the bouncy soles of athletic shoes. They're designed to take a beating and keep on springing!
But Wait, There's More! (The Formula!)
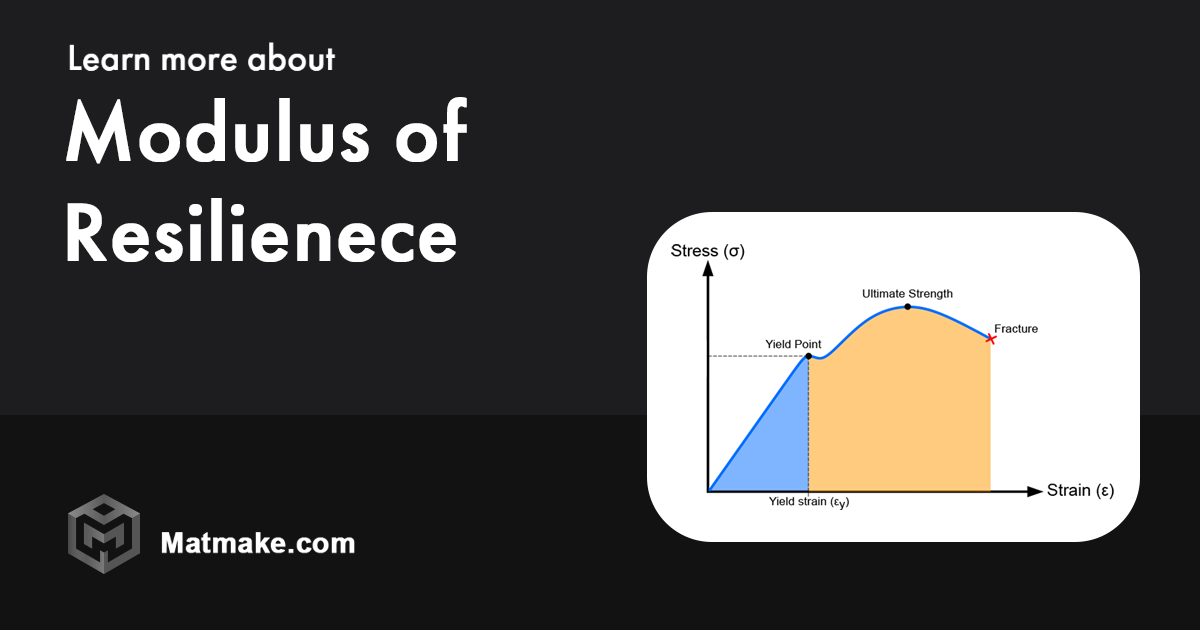
Okay, I know formulas can be a little scary, but trust me, this one's pretty cool. The modulus of resilience (often denoted as Ur) is calculated as: Ur = (σy2) / (2E). Where σy is the yield strength (how much stress it can take before it starts to permanently deform), and E is the Young's modulus (a measure of its stiffness).
Don't let the Greek letters intimidate you! It's just a fancy way of saying that materials that are both strong *and* flexible are the most resilient. It’s the sweet spot between being able to take a punch (high yield strength) and being able to bend without breaking (low Young's modulus). It's like a material doing the limbo under stress!
Materials scientists are constantly searching for materials with a higher modulus of resilience. These materials can be used to make lighter, stronger, and more durable products. Imagine a world with cars that are virtually indestructible or buildings that can withstand earthquakes! The modulus of resilience is a key to unlocking that future.
Why Should You Care?
Because it's everywhere! From the phone in your pocket to the car you drive, the modulus of resilience plays a crucial role in the performance and durability of the things you use every day. Understanding it, even a little bit, gives you a peek into the fascinating world of materials science and the ingenious ways engineers design the world around us.
So next time you see something bounce back, remember the modulus of resilience. It's a testament to the power of materials science and the amazing properties of the stuff that makes up our world. It’s a fun topic to think about and might even inspire you to learn more about the exciting field of material science. Who knows, maybe you will find the next great super material!
The future is built on resilient materials!