We're all fascinated by extremes, aren't we? Whether it's the tallest mountain, the deepest ocean trench, or the spiciest chili pepper, there's something undeniably captivating about pushing boundaries. And in the world of chemistry, one way to explore those boundaries is by looking at the elements themselves. Today, let's embark on a journey to the far end of the periodic table and uncover the secrets of the heaviest alkali metal: Francium!
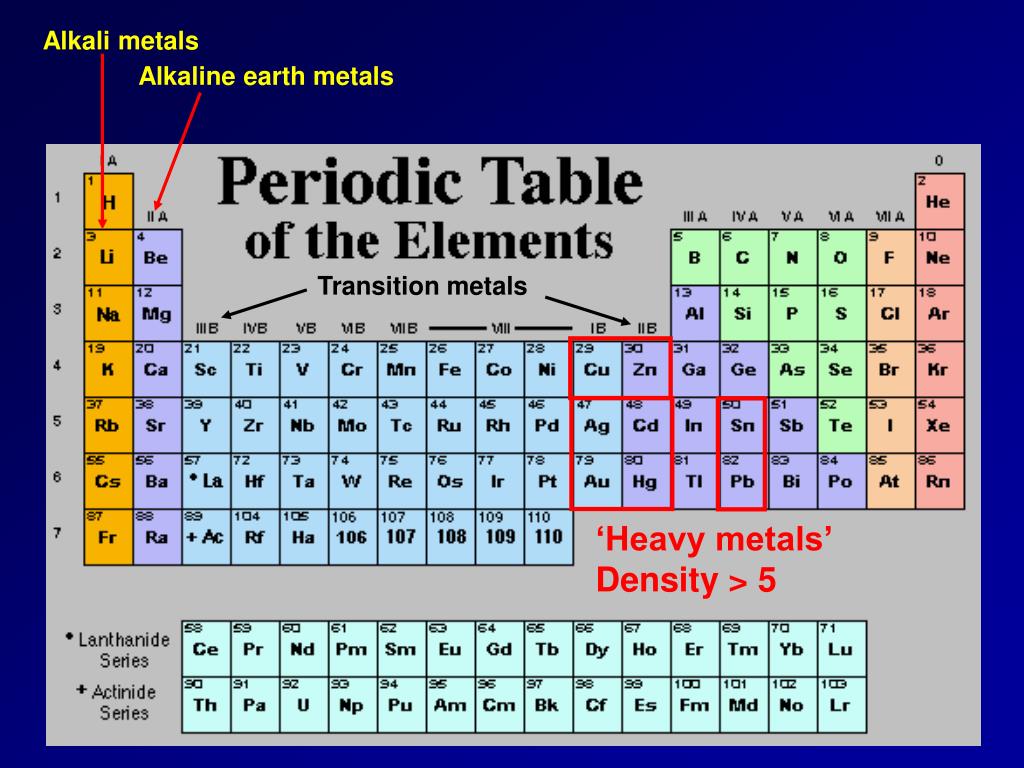
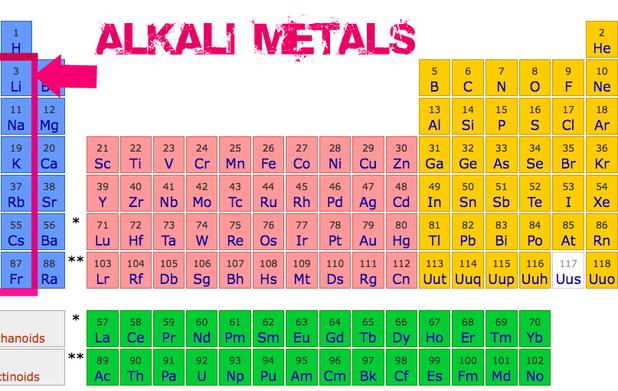
Okay, maybe Francium isn't exactly a household name. You probably won't find it listed in your multi-vitamin ingredients or starring in a dazzling fireworks display. But understanding Francium, and the alkali metals in general, gives us a crucial insight into the fundamental building blocks of the universe. These elements, found in Group 1 of the periodic table (excluding hydrogen, which is a bit of a rebel!), share a common characteristic: they are incredibly reactive. This reactivity stems from their eagerness to lose a single electron, allowing them to form strong bonds with other elements. This, in turn, influences all sorts of processes around us.
Now, you might be thinking, "So what? Why should I care about some obscure element lurking at the bottom of the periodic table?" Well, consider this: while Francium itself doesn't have many direct applications (we'll get to why in a bit!), its lighter cousins are vital to modern life. Lithium powers our smartphones and electric vehicles. Sodium is essential for nerve function and maintaining fluid balance in our bodies – not to mention, it's half of table salt! Potassium plays a similar role in our bodies and is a crucial nutrient for plant growth, making it a key ingredient in fertilizers. Even Rubidium and Caesium, which are further down the group, have applications in atomic clocks and research.
So, what makes Francium special, and why isn't it powering our toasters? The answer lies in its radioactivity. Francium is incredibly unstable, meaning it decays rapidly into other elements. In fact, the longest-lived isotope of Francium has a half-life of only 22 minutes! This makes it exceptionally rare and difficult to study. Scientists have only ever been able to produce tiny amounts of it at a time, making practical applications virtually impossible. Its fleeting existence means we can't harness its power in the same way we do with its lighter relatives.
However, studying Francium, even in these tiny quantities, provides invaluable information about atomic structure and the fundamental forces of nature. By observing how it decays and interacts with other particles, scientists can refine our understanding of the Standard Model of particle physics. It's like studying a supernova – it may be a rare and fleeting event, but it teaches us profound lessons about the cosmos.
While you can't exactly "enjoy" Francium in the traditional sense, you can appreciate its significance by learning more about the periodic table and the elements that make up our world. Exploring interactive periodic tables online, reading articles about interesting elements, and watching documentaries about chemistry are great ways to deepen your understanding and appreciate the fascinating world of elements. Perhaps you'll even discover your own favorite element, radioactive or not!