Ever wondered what it takes to turn solid lead into a vaporous cloud? Get ready to crank up the heat! We're diving into the fascinating world of boiling points, specifically, the boiling point of lead. Buckle up, because it's going to be hot!
The Big Number: Boiling Lead
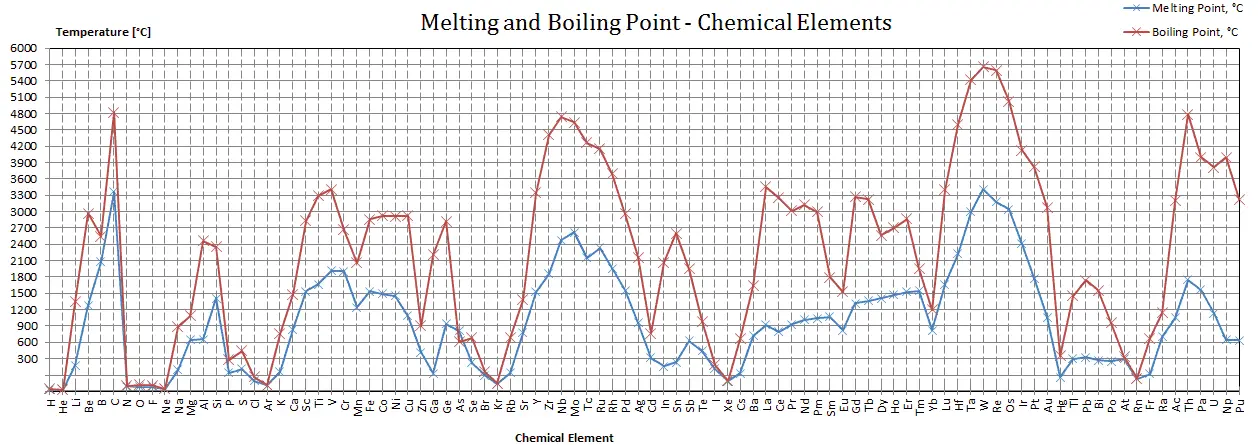
Okay, let's get straight to the point. The boiling point of lead is a scorching 1,749 degrees Celsius (3,180 degrees Fahrenheit). That's seriously hot! You definitely wouldn't want to stick your hand in that.
Think about this: water boils at a measly 100°C (212°F). Lead needs almost 18 times more energy to make the jump from liquid to gas. Talk about demanding!
Why Such a High Temperature?
What makes lead so stubbornly solid? It all boils down (pun intended!) to the strength of the bonds between its atoms. Lead atoms like to stick together, and it takes a lot of energy to break those bonds and let them float freely as a gas.
Imagine it like a group of friends holding onto each other tightly. You'd need a lot of force to pull them apart, right? That's kind of like what's happening with lead atoms.
These atomic bonds are strong because of the unique electron structure of lead. The electrons, which are responsible for bonding, are held more tightly than in many other metals.
Lead's Personality: A Heavyweight Champion
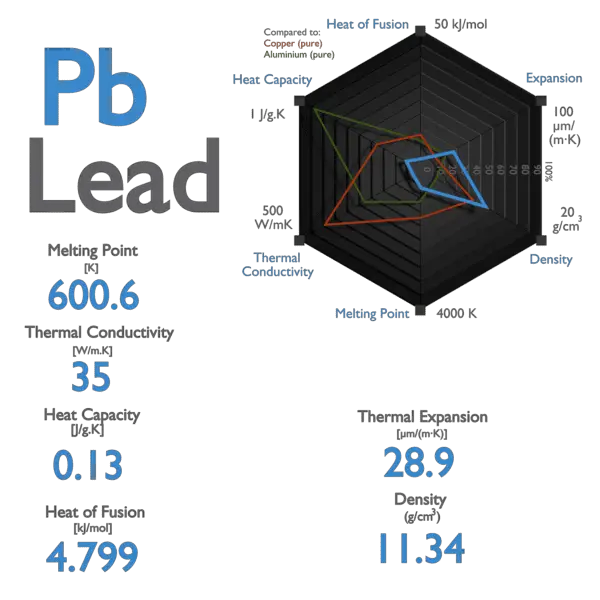
Lead is known for being a heavy metal. This means its atoms are packed closely together. This high density contributes to its high boiling point.
It's not just heavy; it's also relatively unreactive. It doesn't easily combine with other elements. This makes it durable and stable.
Think of lead pipes in old buildings. They last for ages! This inherent stability translates to a high resistance to change of state, hence the high boiling point.
Lead Through the Ages: From Ancient Aqueducts to Modern Batteries
Lead has been used by humans for thousands of years. Ancient Romans used it for plumbing, believing it was safe and easy to work with.
Today, we know about the dangers of lead poisoning. Its usage is carefully regulated. Now it's common in car batteries and radiation shielding.
Understanding its properties, including its high boiling point, is essential for using it safely and effectively. It's all about respecting the material!
Boiling Lead: A Visual Spectacle (If You Could See It Safely)
Imagine, for a moment, being able to safely observe lead as it boils. It would be a mesmerizing sight. A shimmering pool of molten metal transforming into a dense, heavy vapor.
The vapor would probably have a bluish tint. It would slowly dissipate into the atmosphere (hopefully contained in a safe lab environment!). This mental image is quite dramatic.
Unfortunately, breathing lead vapor is extremely dangerous. So, let's stick to imagining it, shall we? Safety first!
The Challenges of Working with Molten Lead
Working with molten lead is not for the faint of heart. The extreme temperatures require specialized equipment and protective gear.
Think of thick gloves, face shields, and well-ventilated areas. It's a serious business!
Even with precautions, there's always a risk of spills and burns. So, it's best left to trained professionals.
Why Bother Knowing This Stuff?
Why is knowing the boiling point of lead important, anyway? It's not exactly a common trivia question at parties (or maybe it is, depending on your parties!). There are plenty of good reasons!
Understanding the properties of elements helps us design and build things safely. It's crucial in many industrial processes. The high boiling point of lead, for example, is critical in lead-acid battery production.
It informs our decisions about which materials to use in different applications. Should we use lead for pipes? Probably not, given its toxicity. But for radiation shielding? It's a great choice!
Beyond Lead: Exploring Other Boiling Points
Once you start thinking about boiling points, you'll realize how fascinating they are! Every element has its own unique boiling point, reflecting its atomic structure and bonding properties.
Helium, for example, has the lowest boiling point of any element: -269°C (-452°F). It's a super-cooled gas that defies easy liquefaction!
Tungsten, on the other hand, has one of the highest boiling points: 5,555°C (10,031°F). It's incredibly heat resistant and used in light bulb filaments.
The Science of Phase Transitions
Boiling is an example of a phase transition. This is a change in the physical state of a substance. Think solid, liquid, and gas.
Melting is another common phase transition. It's the process of a solid turning into a liquid. Freezing is the opposite: liquid to solid.
Sublimation is when a solid turns directly into a gas, skipping the liquid phase altogether! Dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) does this.
Heat of Vaporization: The Energy Required to Boil
The heat of vaporization is the amount of energy required to turn a liquid into a gas at a constant temperature. It's measured in joules per mole (J/mol).
Lead has a relatively high heat of vaporization, reflecting the strong bonds between its atoms. More energy is needed to break them apart.
This property, combined with the high boiling point, underscores the energy-intensive nature of vaporizing lead. It's not a casual process!
Lead in History: From Pipes to Paint
Lead has a long and complicated history with humanity. It was widely used in ancient times, but its toxicity wasn't fully understood.
Roman aqueducts, for example, were made of lead. This likely contributed to lead poisoning among the Roman population.
Lead paint was common for centuries. It provided a durable and vibrant finish. However, it was later found to be a major source of lead exposure, especially for children.
Modern Regulations and Lead Abatement
Today, there are strict regulations regarding the use of lead. Lead paint is banned in many countries. Efforts are underway to remove lead pipes from older buildings.
Lead abatement is the process of removing lead hazards from a property. It's a specialized field that requires careful planning and execution.
Protecting public health from lead exposure is a top priority. Science is essential to making this happen!
So, What Did We Learn About Lead?
Hopefully, you now have a better understanding of the boiling point of lead and why it's so high. It's a fascinating example of how atomic properties influence the macroscopic behavior of materials.
From its heavy density to its relatively unreactive nature, lead has many unique characteristics. It is important to understand them.
So, the next time you hear someone mention lead, you can impress them with your knowledge of its boiling point. And you can remind them to stay safe!