Ever wonder about the stuff that seems to be popping up everywhere, promising to be better for the planet? You might have heard of it: PLA, or Polylactic Acid. But what *is* it, really? It sounds like something cooked up in a lab (and, well, it kind of is!), but the really cool thing is that it often starts with something incredibly common: plants! Learning about PLA is fun because it shows us how we can rethink everyday materials and maybe even make a dent in some big environmental problems.
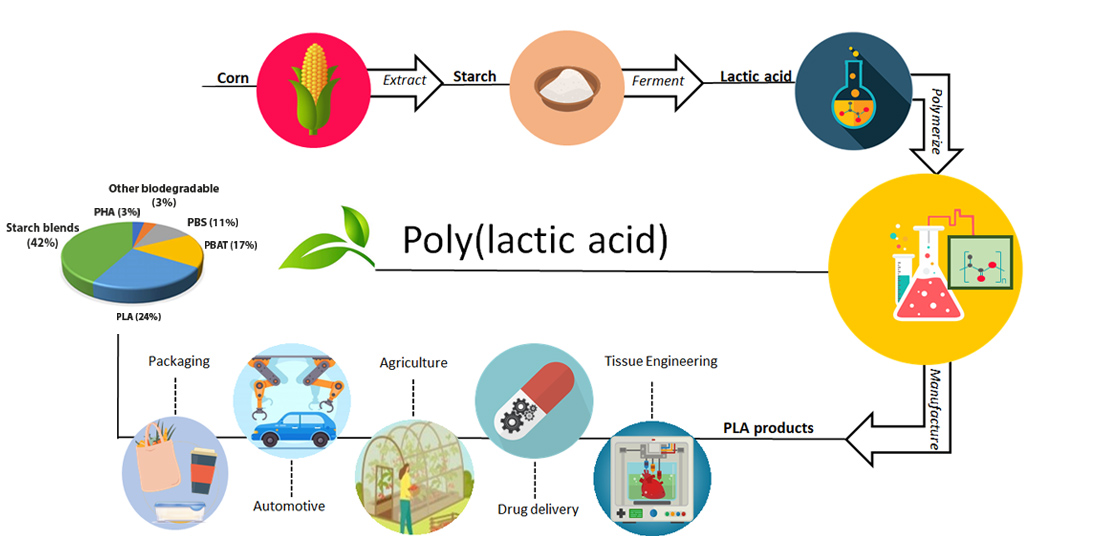
So, what's the big deal with PLA? Its main purpose is to be a biodegradable alternative to traditional plastics derived from petroleum. Traditional plastics stick around for hundreds of years, clogging landfills and harming ecosystems. PLA, on the other hand, can break down under the right conditions – typically in industrial composting facilities. This makes it a more sustainable option for a variety of applications. One of the key benefits is its reduced reliance on fossil fuels, which helps lower our carbon footprint. It's also generally considered food-safe, which is a huge plus when it comes to packaging.
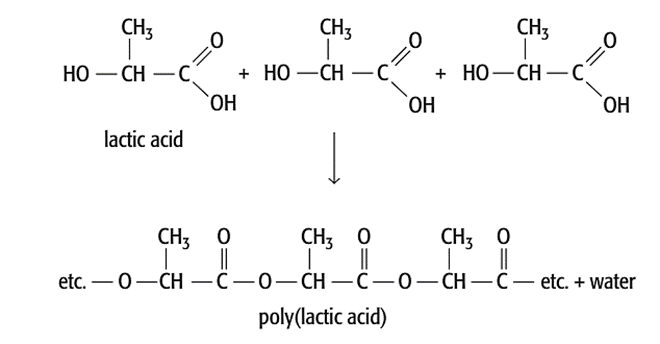
Now, let's get down to the nitty-gritty: What's it actually made from? The process usually starts with plant-based sources like corn starch, sugarcane, or even cassava roots. These are rich in starch or sugars. The starch or sugar is then fermented, much like brewing beer! This fermentation process creates lactic acid. The lactic acid molecules are then linked together to form long chains, creating polylactic acid – PLA! It's a bit of chemistry magic, transforming something simple like corn into a versatile material.
You're probably already encountering PLA in your daily life, perhaps without even realizing it. In education, many 3D printers use PLA filament. It's a safer and more environmentally friendly option for classrooms. Think about the last time you grabbed a “compostable” coffee cup lid or a clear container from a deli. There's a good chance it was made from PLA. You might also find it in disposable cutlery, food packaging, and even some clothing fibers! It's also used in some medical implants, as it can safely dissolve in the body over time.
Want to explore PLA further? Here are a few simple things you can do: First, start paying attention to the packaging of products you buy. Look for labels that say "PLA," "compostable," or "made from plants." Once you find something made of PLA, try to find out where you can properly compost it in your area. Not all composting facilities accept PLA, so it’s important to check. If you have access to a 3D printer, experiment with different colors and types of PLA filament. You can even find PLA filaments made from recycled materials! The more we understand about materials like PLA, the better equipped we are to make informed choices that benefit both ourselves and the planet. It's a small step, but it can make a big difference.