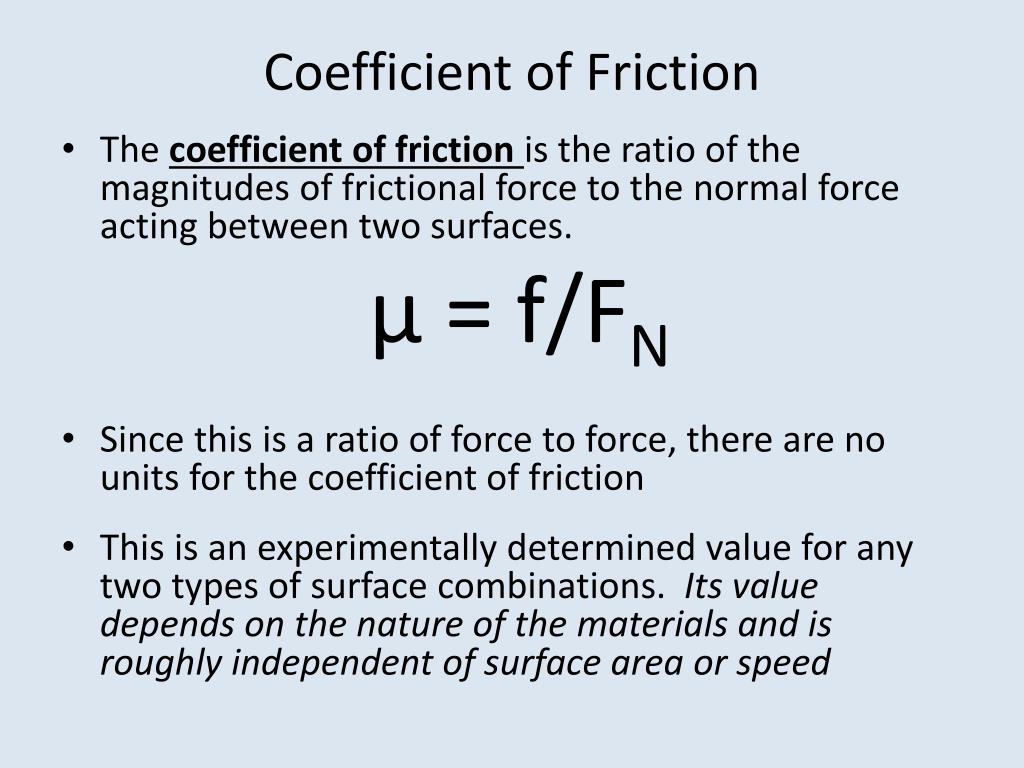
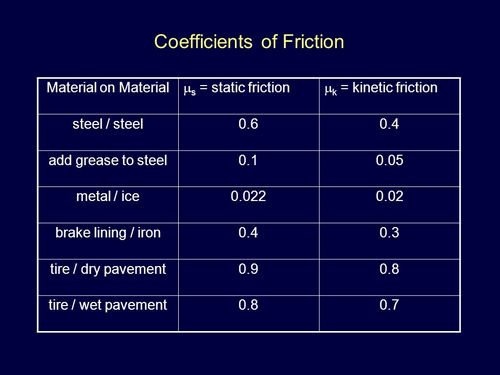
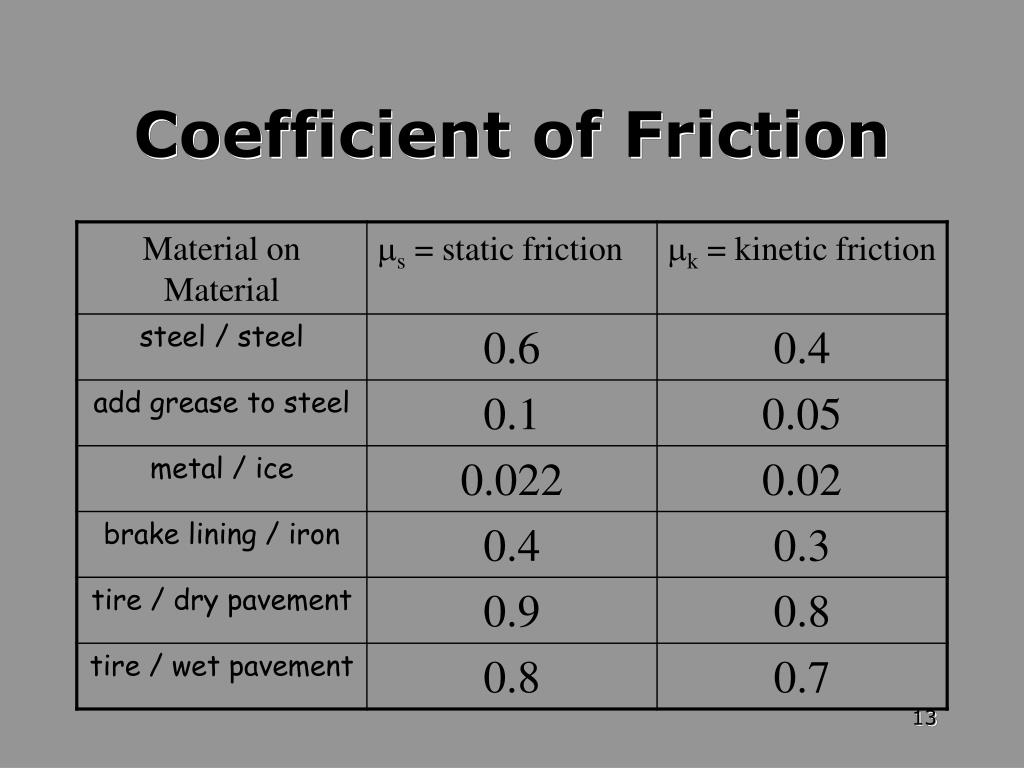
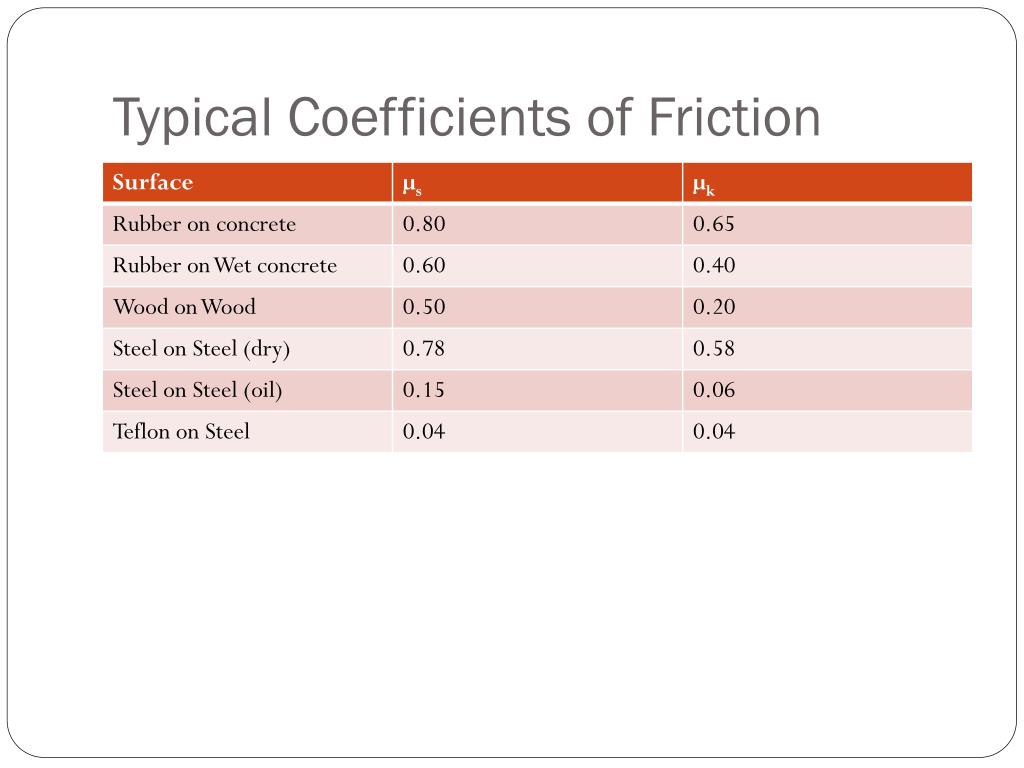
Have you ever tried to walk on an icy sidewalk wearing your favorite smooth-soled shoes? Or maybe you've watched a cartoon character hilariously struggle to pull a heavy box across a slick floor? If so, you've already encountered the coefficient of friction – even if you didn't know its fancy name.
Friction: The Unseen Force
Imagine friction as the grumpy little troll that lives between two surfaces, always trying to make things difficult. Whenever you try to slide one thing across another, friction is there, pushing back, making you work harder. It's that resistance you feel when you shove a box across the carpet, or the reason your car eventually slows down when you take your foot off the gas. Without friction, the world would be a slippery, chaotic mess! Think of a world without friction... no gripping anything!
So, where does this grumpy troll, friction, get its strength? Well, it depends on a few things. One major factor is how rough or smooth the surfaces are. Think of sandpaper versus glass. Sandpaper is covered in tiny bumps and ridges that catch on anything it touches, creating a lot of friction. Glass, on the other hand, is relatively smooth, so things slide across it more easily. That's why you'd rather use sandpaper to sand something down, and not glass!
Enter the Coefficient of Friction: The Troll's Power Rating
Now, the coefficient of friction is basically a number that tells you just how strong this grumpy troll is. It's like a power rating for friction. A higher number means the troll is super strong and the surfaces are very resistant to sliding. A lower number means the troll is weak and things slide easily. It tells us the ratio of the force required to move an object to the force holding it against the surface. See it as a measure of how much force is needed to overcome friction and start movement.
Think about it this way: Ice skates glide effortlessly on ice because the coefficient of friction between the steel blade and the ice is very low. The "troll" is barely putting up a fight! But if you tried to ice skate on asphalt, the "troll" would be a giant, and you wouldn't go anywhere. Asphalt has a much higher coefficient of friction with steel. That is why we use asphalt for roads and highways!
Fun Facts & Slippery Situations
Here's a fun fact: The coefficient of friction isn't just about the materials involved. It also depends on whether the object is already moving or if it's trying to start moving. Starting friction (static friction) is usually higher than moving friction (kinetic friction). That's why it takes more effort to get a heavy box moving than to keep it moving. The troll is extra stubborn when you first try to wake him up!
Imagine trying to push a car stuck in mud. It takes a herculean effort to get it moving (overcoming static friction), but once it's rolling, it's a little easier to keep it going (overcoming kinetic friction).
The coefficient of friction plays a crucial role in everything from designing car tires to building skyscrapers. Engineers need to understand how different materials will interact with each other to ensure safety and efficiency. For example, they use materials with high coefficients of friction for brake pads to stop your car quickly, but they use materials with low coefficients of friction for engine parts to reduce wear and tear. This makes sure that your car doesn't fall apart, but also stops when you want it to.
Next time you're slipping and sliding on an icy surface, or struggling to open a stubborn jar, remember the grumpy little troll of friction and its power rating: the coefficient of friction. It's a simple concept that explains so much about the world around us, and it's probably a bit more interesting than you ever thought!
And remember, the coefficient of friction isn't just about dry surfaces. It also applies to fluids! This is how boats and airplanes work. Fluid friction is a key part of movement!