Ever wondered about the truly amazing jobs people do in the world? Let's dive deep – quite literally – into the fascinating realm of underwater welding! It's a profession that sounds like something out of a science fiction movie, but it's a very real, and essential, part of modern infrastructure and maintenance.
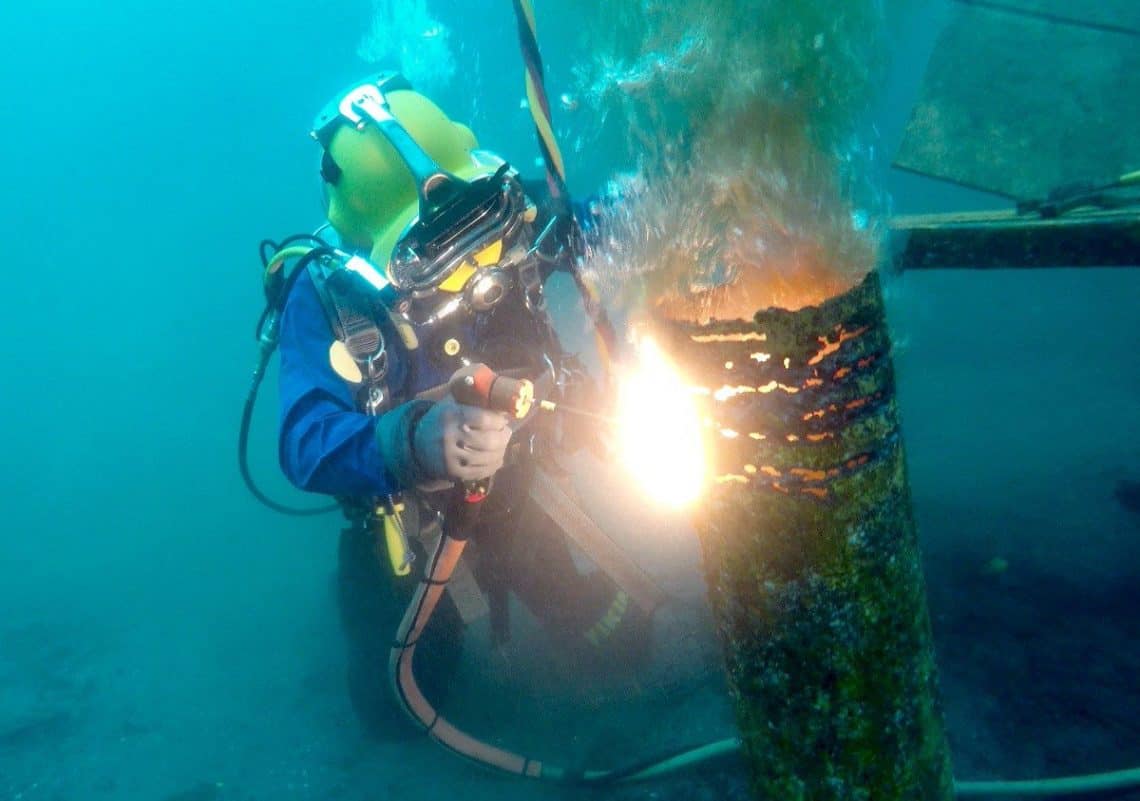
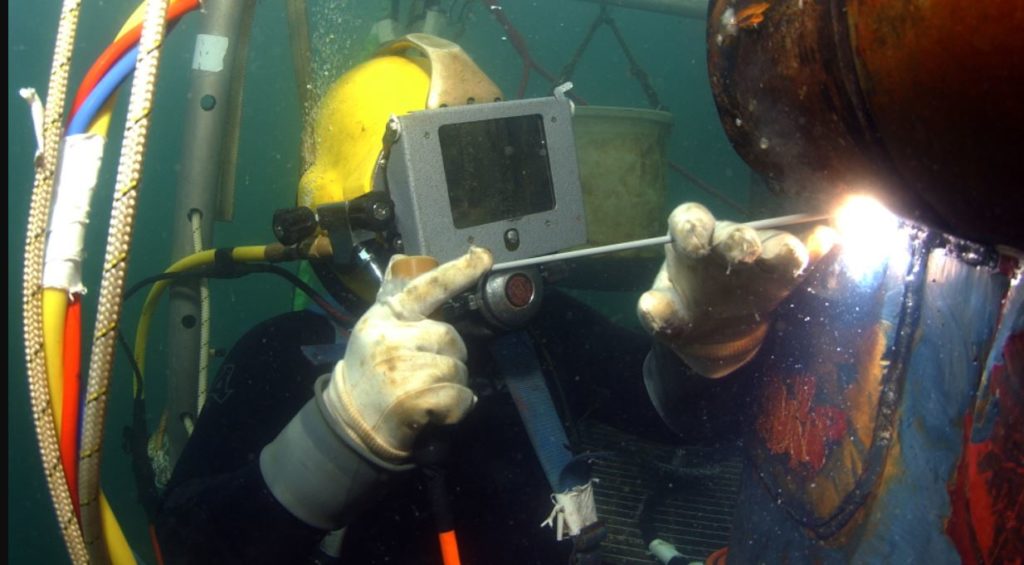
So, what exactly does an underwater welder do? In short, they're highly skilled professionals who perform welding and cutting tasks while completely submerged in water. Think of it like a construction worker or a repair technician, but their worksite is the ocean floor, a riverbed, or even inside a flooded structure. The purpose is clear: to repair, maintain, or construct underwater structures that are vital to our lives.
The benefits of underwater welding are immense. Imagine a pipeline carrying oil or gas across the seabed develops a leak. Taking the entire pipeline out of service for repair on land would be incredibly expensive and disruptive. Underwater welders can quickly and efficiently repair the damage in situ, minimizing downtime and preventing potential environmental disasters. Similarly, they're crucial for repairing ship hulls, maintaining offshore oil platforms, and constructing underwater habitats or tunnels.
The applications are far-reaching. In education, underwater welding techniques are taught at specialized training schools, preparing the next generation of skilled professionals. These courses often incorporate advanced metallurgy, diving physiology, and safety procedures. In daily life, you might not directly see the fruits of their labor, but consider this: underwater welders are essential for maintaining bridges that span rivers, ensuring the structural integrity of dams that provide hydroelectric power, and even constructing the tunnels that allow us to travel underground or under waterways. They’re the unseen heroes keeping our world connected and functioning smoothly.
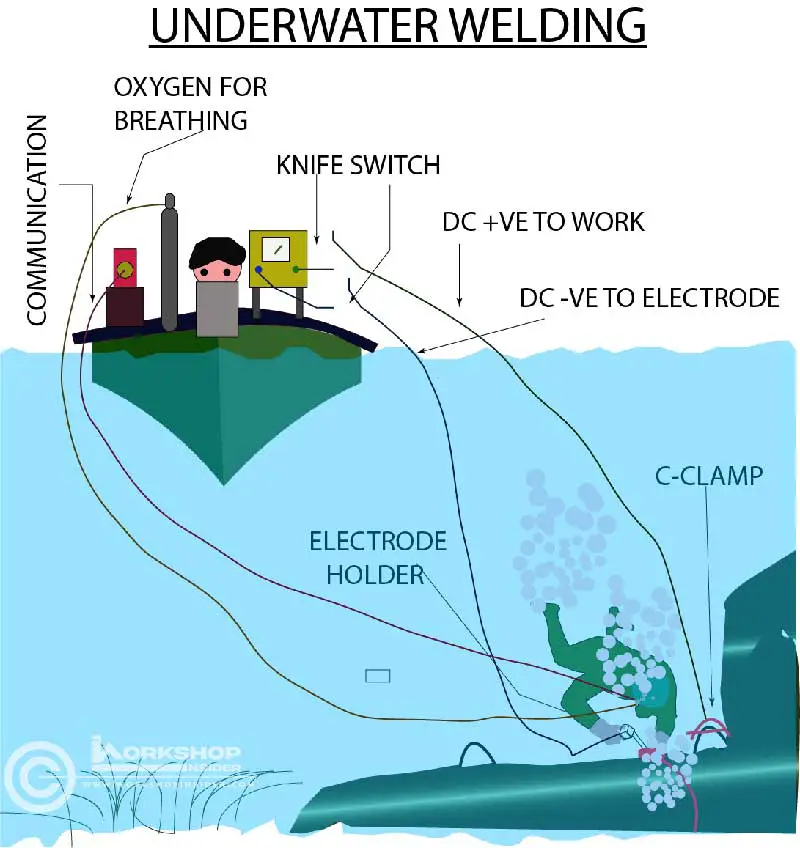
Underwater welding utilizes specialized equipment to create a localized, controlled environment for the welding process. Two main techniques are employed: wet welding, where the welding is performed directly in the water, and dry welding, where a hyperbaric chamber is used to create a dry, pressurized environment around the weld area. Dry welding generally produces higher quality welds but is also more complex and expensive.
Feeling curious and want to explore this field further? While becoming a certified underwater welder requires extensive training, there are simpler ways to dip your toes in (metaphorically speaking, of course!). Research diving techniques and safety protocols. Look into the physics and chemistry of welding – understanding how metals interact and fuse together is fundamental. Watch documentaries or read articles about large-scale underwater construction projects. These little steps can provide a fascinating glimpse into this remarkable profession. And who knows? Maybe one day, you'll be the one wielding the welding torch beneath the waves!