Ever wondered what exactly makes up that water bottle, your favorite toy, or even the dashboard in your car? It's all about plastics, and believe it or not, the chemistry behind them is pretty fascinating! We use plastics constantly, but rarely stop to think about the chemical building blocks that give them their diverse properties. So, let's dive into the world of plastic chemistry – it's more interesting than you might think!
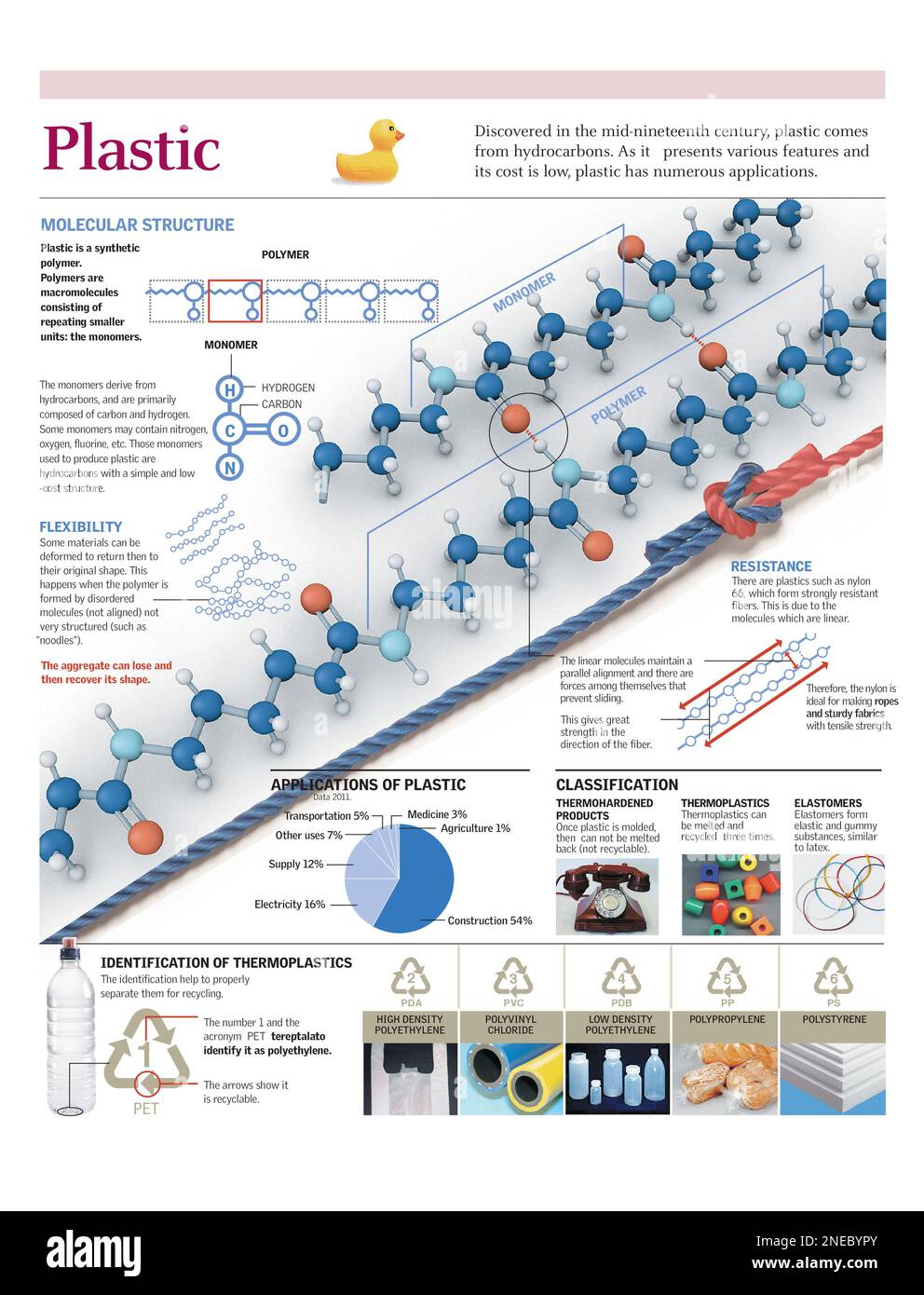
At its heart, plastic is made up of long chains of molecules called polymers. Think of it like a necklace, where each bead is a small molecule called a monomer. These monomers link together in repeating patterns to create the polymer chain. The type of monomer used, and how they're arranged, determines the specific properties of the plastic.
One common monomer is ethylene, derived from petroleum. When ethylene monomers join together, they form polyethylene (PE), which is used to make things like plastic bags, milk jugs, and cling wrap. It's flexible, cheap to produce, and relatively inert, making it perfect for packaging.
Another popular plastic is polyvinyl chloride (PVC). The monomer for PVC is vinyl chloride. PVC is known for its strength and rigidity, so it's often used in pipes, window frames, and even clothing. However, it's also important to note that some plasticizers are added to PVC to make it more flexible.
Then there’s polypropylene (PP), made from the monomer propylene. PP is tough and resistant to chemicals, making it a great choice for containers that hold food, cleaning supplies, and even car parts. It's also used in fibers for things like carpets and ropes.
Polystyrene (PS), created from styrene monomers, is another common plastic. It can be either rigid or foamed. Rigid polystyrene is used in things like disposable cutlery and CD cases, while foamed polystyrene (Styrofoam) is used for insulation and protective packaging.
So, what's the purpose and benefit of all these different plastics? Well, each type of plastic has specific properties that make it ideal for different applications. They are designed to be durable, lightweight, and cost-effective. They can be molded into almost any shape, making them incredibly versatile. Plastics also play a crucial role in hygiene and safety, from sterile medical equipment to protecting food from contamination.
However, it's important to remember that not all plastics are created equal. Some contain additives, like plasticizers (to make them more flexible) or flame retardants, which can potentially leach out of the plastic and pose health concerns. That's why it's important to be mindful of the type of plastic you're using, especially when it comes to food and drinks. Look for recycling codes and try to choose plastics that are generally considered safer, like polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP).
Understanding the chemistry of plastics allows us to make more informed choices about the products we use and their impact on the environment. So, the next time you reach for a plastic item, take a moment to appreciate the amazing science behind it!