Have you ever stopped to wonder what makes fireworks sparkle with such vibrant colors, or what keeps your bones strong and healthy? The answer, in part, lies with a fascinating group of elements known as the alkaline earth metals. Learning about them isn't just about memorizing facts; it's about understanding the building blocks of our world and appreciating the chemistry happening all around us.
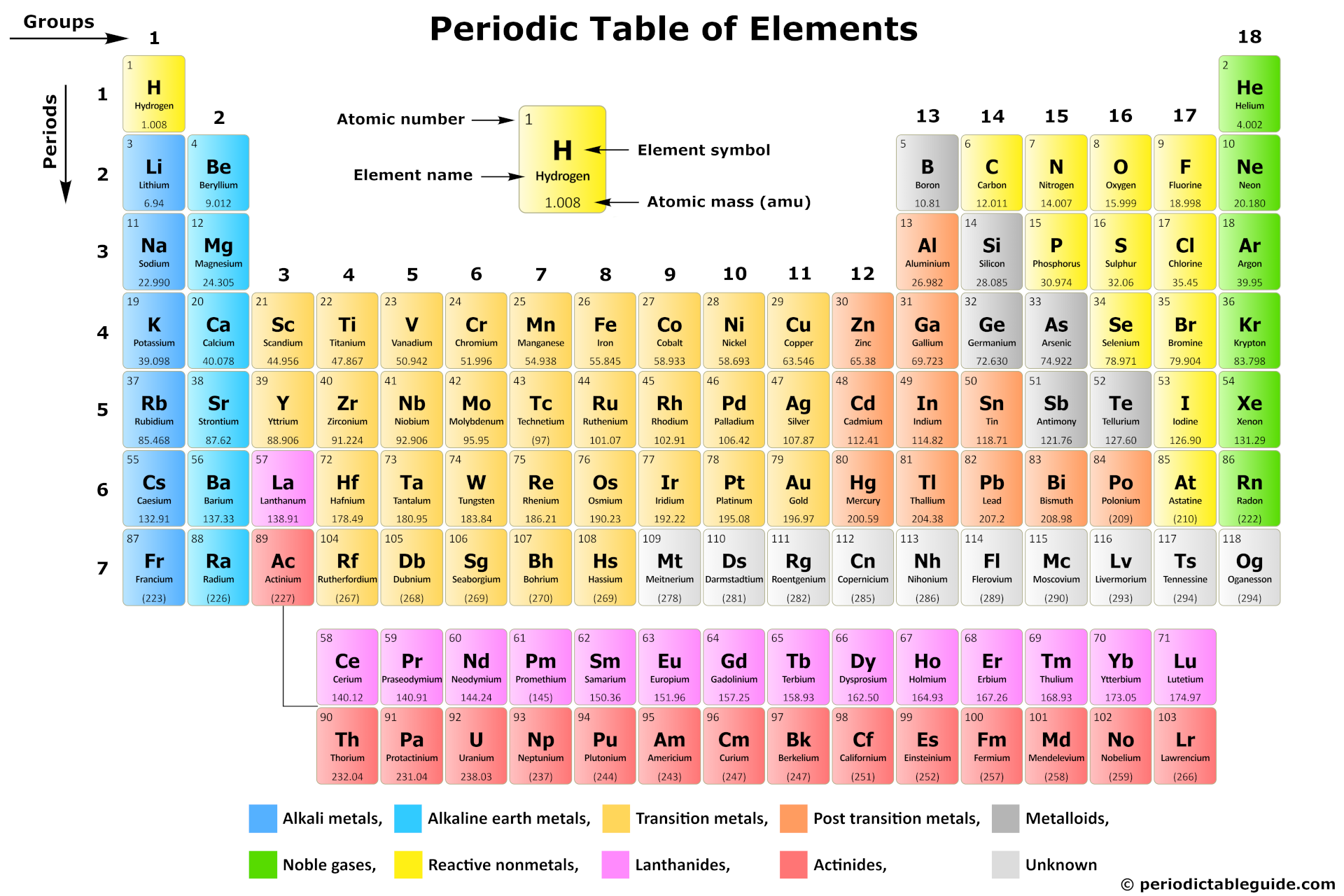
So, what exactly are the alkaline earth metals? They're a family of six elements found in Group 2 of the periodic table: beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra). They're called "alkaline earth metals" because their oxides (compounds with oxygen) form alkaline solutions when dissolved in water, and because early chemists considered them "earths" (a historical term for non-metallic substances that are insoluble in water and resistant to heat).
The purpose and benefits of understanding these elements are surprisingly diverse. Primarily, knowing about them unlocks a deeper understanding of chemical reactivity. Alkaline earth metals are highly reactive, though not as reactive as the alkali metals (Group 1). They readily lose two electrons to form positive ions with a +2 charge. This tendency to react makes them incredibly useful in various applications.
Think about your health, for example. Calcium is essential for strong bones and teeth, as well as nerve function and muscle contraction. You probably learned about this in school, but understanding that calcium is an alkaline earth metal gives you a broader context. Magnesium is another crucial nutrient, playing a role in hundreds of biochemical reactions in your body, including energy production. Epsom salts, used for soothing sore muscles, are actually magnesium sulfate!
The alkaline earth metals also show up in many everyday products. Magnesium is used in lightweight alloys for things like airplane parts and car wheels. Strontium compounds are responsible for the brilliant red colors in fireworks. Barium sulfate is used as a contrast agent in medical X-rays, allowing doctors to see internal organs more clearly. Even beryllium, though toxic in its elemental form, is used in specialized alloys for its strength and resistance to corrosion.
Exploring the alkaline earth metals can be a fun and engaging process. You don't need a laboratory! Start by looking at the labels of food and supplements to see where calcium and magnesium are listed. Research the different compounds of each element and their uses. For example, look up "calcium carbonate" (found in antacids) or "magnesium oxide" (used in some dietary supplements). You can even explore online resources like the Royal Society of Chemistry's website or Khan Academy for more in-depth explanations and interactive lessons. The possibilities for learning are endless!
In conclusion, the alkaline earth metals are a vital group of elements with a wide range of applications, from keeping our bodies healthy to creating stunning displays of pyrotechnics. By learning about them, we gain a greater appreciation for the chemistry that shapes the world around us and the amazing properties of the elements.

.png)

