Hey there! Ever wondered where all that electricity powering your phone, your fridge, and, let's be honest, your late-night Netflix binge comes from? A big chunk of it is likely generated in power plants, and among those, nuclear power plants stand out. They're a bit like the silent giants of the energy world – powerful, but also a bit mysterious. Let's unpack the good, the bad, and the slightly radioactive of nuclear power, shall we?
The "Good Stuff": Why Nuclear Power Gets a Thumbs Up
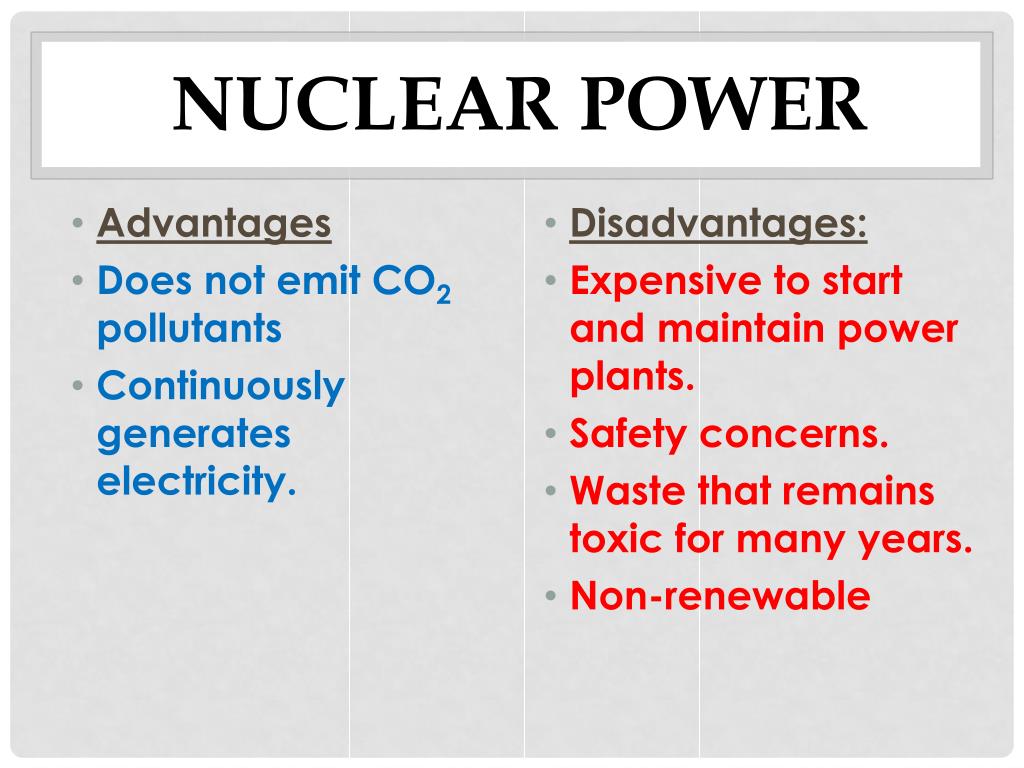
First up, let's talk about the advantages – the reasons why nuclear power is often touted as a valuable energy source. Think of it like this: imagine you're baking cookies. Nuclear power is like having a super-efficient oven that bakes tons of cookies (electricity) with just a tiny bit of fuel. And the best part? It doesn't puff out smoke (carbon emissions) while doing it!
* Low Carbon Emissions: This is the big one! Nuclear power plants produce very little greenhouse gas during operation. Compare it to driving an electric car charged by renewable energy – you're not contributing to air pollution like you would with a gas-guzzler. We're talking about significantly less pollution than coal or even natural gas power plants. In a world grappling with climate change, that’s a huge win.
* Reliable and Consistent: Unlike solar and wind power, which depend on the weather, nuclear power plants can operate 24/7, rain or shine. Think of it as having a steady paycheck versus relying on tips – you know you're going to have a certain amount coming in, regardless of external factors. This reliability is crucial for keeping the lights on and our economy humming.
* High Power Output: Nuclear power plants can generate a lot of electricity from a relatively small amount of fuel. A single uranium pellet, about the size of your fingertip, contains the same amount of energy as approximately 17,000 cubic feet of natural gas, 1,780 pounds of coal or 149 gallons of oil! That's some serious energy density.
* Energy Independence: For countries that have uranium resources, nuclear power can reduce reliance on foreign energy sources. It's like growing your own vegetables in your backyard – you're less dependent on the grocery store (or, in this case, other countries) for your needs.
The "Not-So-Good Stuff": The Downsides of Nuclear Power
Now, let's address the elephant in the room – the disadvantages. Nuclear power, despite its benefits, comes with its own set of challenges.
* Nuclear Waste: This is arguably the biggest concern. Nuclear power plants produce radioactive waste that remains hazardous for thousands of years. Think of it as a really, really stubborn stain that refuses to come out, no matter what you try. We need safe and permanent ways to store or dispose of this waste, and finding these solutions is a complex and ongoing process.
* Accident Risk: While nuclear power plants are designed with multiple safety features, accidents can happen, as we saw at Chernobyl and Fukushima. These accidents can release radiation into the environment, causing long-term health and environmental damage. It's like a kitchen fire – unlikely, but devastating if it happens. Continuous safety improvements are paramount.
* High Initial Costs: Building a nuclear power plant is incredibly expensive. We're talking billions of dollars! This can make it difficult to attract investment and can drive up the cost of electricity. It's like buying a fancy new car – it might be great in the long run, but the upfront cost can be a significant barrier.
* Security Concerns: Nuclear materials could potentially be targeted by terrorists. Robust security measures are essential to prevent theft or sabotage. It's like having a really valuable painting – you need to protect it from being stolen or damaged.
Why Should You Care?
So, why should you, the average person scrolling through the internet, care about all this nuclear power stuff? Because it affects everyone! It impacts the air we breathe, the energy we use, and the future of our planet. The decisions we make about energy sources will determine what kind of world we leave for future generations.
Think about it: cleaner air means fewer respiratory problems. A reliable energy grid means fewer power outages. And a stable climate means a more predictable and sustainable future. Nuclear power, with all its pros and cons, is a key piece of this puzzle.
Ultimately, the future of nuclear power depends on careful consideration of its advantages and disadvantages, ongoing research and development, and informed public dialogue. It's not a simple "yes" or "no" answer – it's a complex issue with profound implications. So, stay informed, ask questions, and be part of the conversation!