Okay, picture this: I'm in my garage, right? Covered in more grime than a mechanic who's just rebuilt an engine with his bare hands. I'm trying to cut through this ridiculously thick piece of steel for a totally awesome (in my head, at least) art project. And my oxy-acetylene torch? It's sputtering, hissing, and generally acting like it wants a divorce. I'm thinking, "Seriously? Now? Of all the times?" Turns out, a tiny little O-ring had decided to stage a rebellion. That's when I realized, I needed a serious refresher on exactly what all those parts on my torch do.
So, if you've ever found yourself staring blankly at your cutting torch, wondering if it's possessed, or if you just want to understand your tools a little better, you're in the right place. Let's break down the anatomy of an oxy-acetylene cutting torch, shall we?
The Body: The Foundation of Fire-Breathing Power
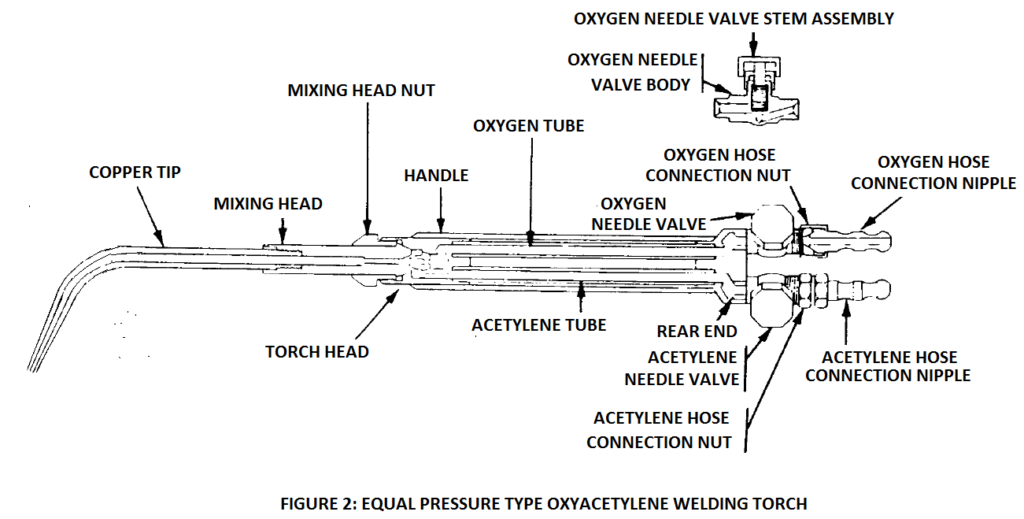
First, we have the torch body. This is basically the main handle, the central hub where everything connects. Think of it as the quarterback of your cutting team. It's usually made of brass or some other durable metal to withstand the heat and pressure. It houses the control valves, which are super important.
(Seriously, treat this part with respect. A damaged body can mean leaks and that’s a big no-no with flammable gases!)
Control Valves: Taming the Flames
Speaking of control valves, these are how you adjust the flow of oxygen and acetylene. Each gas has its own valve, usually color-coded (oxygen is typically green, acetylene is red). Cranking these open and closed dictates the size and intensity of your flame. Too much acetylene? Sooty, black flame. Too much oxygen? Oxidizing flame that can ruin your cut. It's all about finding that sweet spot, that perfect balance for a neutral flame.
Pro Tip: Always double-check your valves before you start cutting. And never force them! If they're stuck, something's probably wrong.
The Mixer: Where the Magic Happens
The mixer is, well, where the oxygen and acetylene mix. It’s usually located inside the torch head. This is a critical part, as the quality of the mix directly affects the quality of your cut. A poorly mixed gas can lead to uneven heating and a messy, ragged cut. Nobody wants that!
Think of the mixer as the bartender of your torch – getting the proportions just right is key to a good result. (Okay, maybe a *slightly* dangerous bartender…)
The Cutting Tip: The Point of Attack
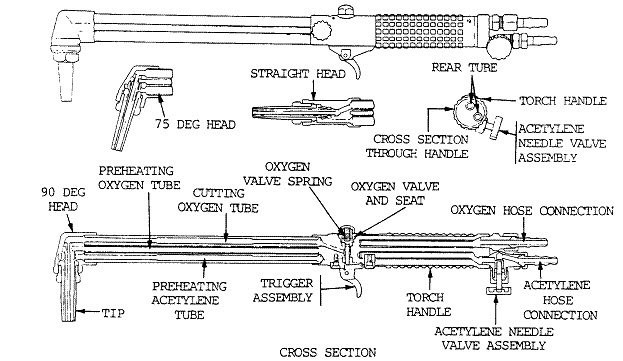
Now, onto the cutting tip. This is the business end of the torch, where the mixed gases ignite and create the cutting flame. Cutting tips come in various sizes and configurations, depending on the thickness and type of metal you're cutting. They have a central oxygen orifice surrounded by preheating orifices. The preheating flames heat the metal to its ignition temperature, and then the high-pressure oxygen stream from the center orifice does the actual cutting by oxidizing the metal. It's like a tiny, controlled inferno.
Different metals need different tips. Using the wrong tip is like trying to cut a cake with a butter knife – frustrating and ineffective. Plus, you'll waste a ton of gas.
Hoses: Delivering the Goods
We can't forget the hoses! These are the lifelines that supply the oxygen and acetylene from the tanks to the torch. They're usually made of reinforced rubber and are color-coded to match the gas they carry. Always check your hoses for cracks, leaks, or wear before each use. A leaky hose is a recipe for disaster.
(Think of them like arteries. Keep 'em healthy!)
Check Valves: Preventing Backflow
These often-overlooked heroes are usually located at either the regulator end of the hose, or the torch itself, or sometimes both! Check valves prevent gases from flowing backward through the hoses and potentially mixing in the regulators or gas tanks. This is super important because mixing oxygen and acetylene in the wrong places can create an explosive situation. Check valves act like one-way streets for your gases.
Safety First! Seriously, don't skimp on these. They’re a small investment that can save you a whole lot of trouble (and potentially your eyebrows).
The Regulator: Keeping the Pressure Under Control
While not strictly *on* the torch, regulators are a vital part of the oxy-acetylene setup. They attach to the gas cylinders and reduce the high pressure inside the cylinders to a usable working pressure for the torch. They also maintain a constant pressure, which is essential for a consistent cut. Messing around with a regulator you don’t understand is a bad idea. If you are unsure, seek a professional.
So, there you have it – a whirlwind tour of the oxy-acetylene cutting torch parts. Now, the next time your torch starts acting up, you'll be able to troubleshoot like a pro (or at least know where to start looking). And remember, safety is paramount. Always wear proper PPE (personal protective equipment), read the manufacturer's instructions, and if you're ever unsure about something, seek advice from a qualified professional. Happy cutting!