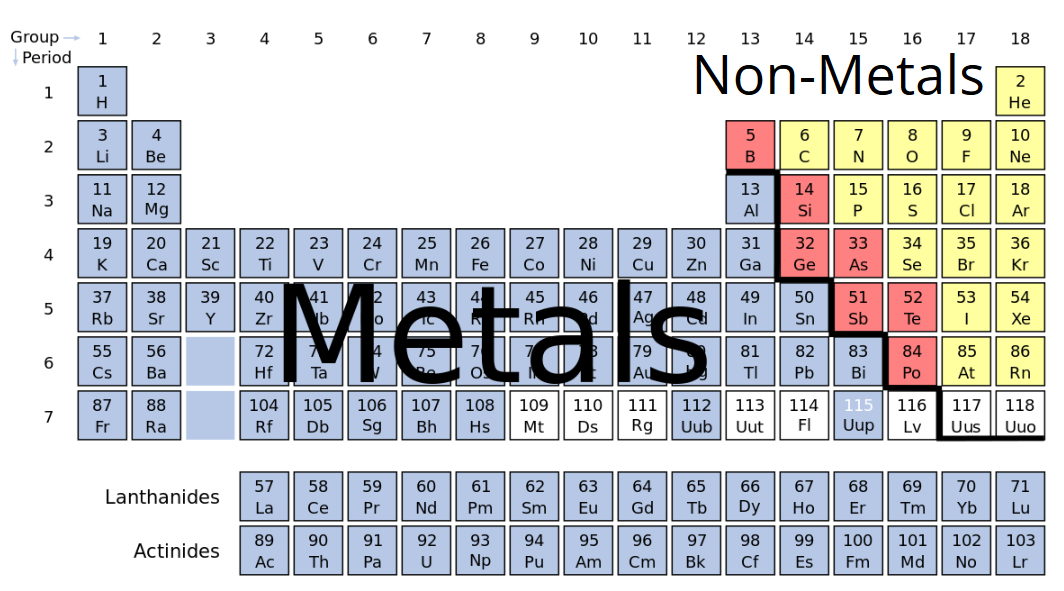
Ever wondered what makes your soda can so…canned? Or why your favorite bicycle frame is so light yet strong? The answer often boils down to a single element: Aluminum. But that begs the question, is aluminum a metal or a nonmetal? It's a question that might seem dry, but understanding it unlocks a world of appreciation for the materials that shape our everyday lives. Let's dive in and see why this shiny stuff is actually quite interesting!
So, is it metal or nonmetal? The short answer is: aluminum is definitely a metal. But that’s not the whole story! Knowing *why* it's a metal is more helpful. For beginners, understanding the difference between metals and nonmetals is a foundation for learning about chemistry and materials science. Metals are generally shiny, good conductors of electricity and heat, and malleable (meaning they can be hammered into shapes). Think of copper wires carrying electricity, or a blacksmith shaping iron. Nonmetals, on the other hand, tend to be dull, poor conductors, and brittle. Think of charcoal or sulfur.
For families, consider the cooking pots and pans in your kitchen. Many are made from aluminum, or have an aluminum core. Its excellent heat conductivity allows for even cooking, preventing hot spots that can burn food. Plus, it's relatively lightweight, making those larger pots easier to handle. Knowing that aluminum is a metal explains *why* it works so well in these applications. It also helps in understanding recycling – aluminum is highly recyclable, retaining its properties even after repeated processing, making it an environmentally friendly choice. Knowing this can spark conversations about sustainability within the family.
Hobbyists, especially those into DIY projects or model making, will appreciate aluminum's versatility. It's relatively easy to work with, can be cut, drilled, and formed, and is resistant to corrosion. Think about building a miniature robot frame, crafting custom brackets, or even creating decorative art pieces. Different alloys of aluminum exist, offering varying degrees of strength and workability. For example, 6061 aluminum is a common choice for structural applications due to its strength and weldability, while softer grades are easier to shape for artistic purposes.
Examples of aluminum's widespread use are everywhere. From the foil in your kitchen to the airplanes soaring overhead, aluminum plays a crucial role. Variations include aluminum oxide, a protective layer that naturally forms on the surface of aluminum, preventing corrosion. This is why aluminum doesn't rust like iron. Anodized aluminum is another variation where this oxide layer is artificially thickened for enhanced protection and aesthetic appeal, often seen in brightly colored phone cases or cookware.
Want to explore aluminum further? Here are a few simple, practical tips: Start by observing aluminum objects around you. Notice their properties – are they shiny? Are they lightweight? Try bending a piece of aluminum foil (carefully!) to see how malleable it is. Research different aluminum alloys online and learn about their specific properties. For a fun experiment, try building a simple circuit using aluminum foil as a conductor. Remember to always prioritize safety when working with electricity.
So, while the question "Is aluminum a metal or a nonmetal?" might seem basic, the answer opens a doorway to understanding the world around us. By recognizing aluminum as a metal and appreciating its unique properties, you gain a greater appreciation for the ingenuity and innovation that shapes our daily lives. Enjoy exploring the wonderful world of materials!