Ever wonder how much power your favorite gadgets are *actually* using? Understanding watts and kilowatt-hours might sound like something only electricians need to worry about, but it's surprisingly fun – and super useful for anyone who wants to save money on their electricity bill. Thinking about watts and kilowatt-hours is like unlocking a secret code to understanding your home's energy use. Ready to crack it?
So, how many watts *are* in a kilowatt-hour? The short answer is: it's a bit of a trick question! A kilowatt-hour (kWh) isn't actually measuring watts directly. Watts measure power – the rate at which energy is being used *at a specific moment*. A kilowatt-hour measures energy consumption – how much power you've used over a period of time, specifically, one hour. Think of it like this: watts are like your car's speedometer showing how fast you're going *right now*, while kilowatt-hours are like your trip odometer, showing how far you've driven in total.
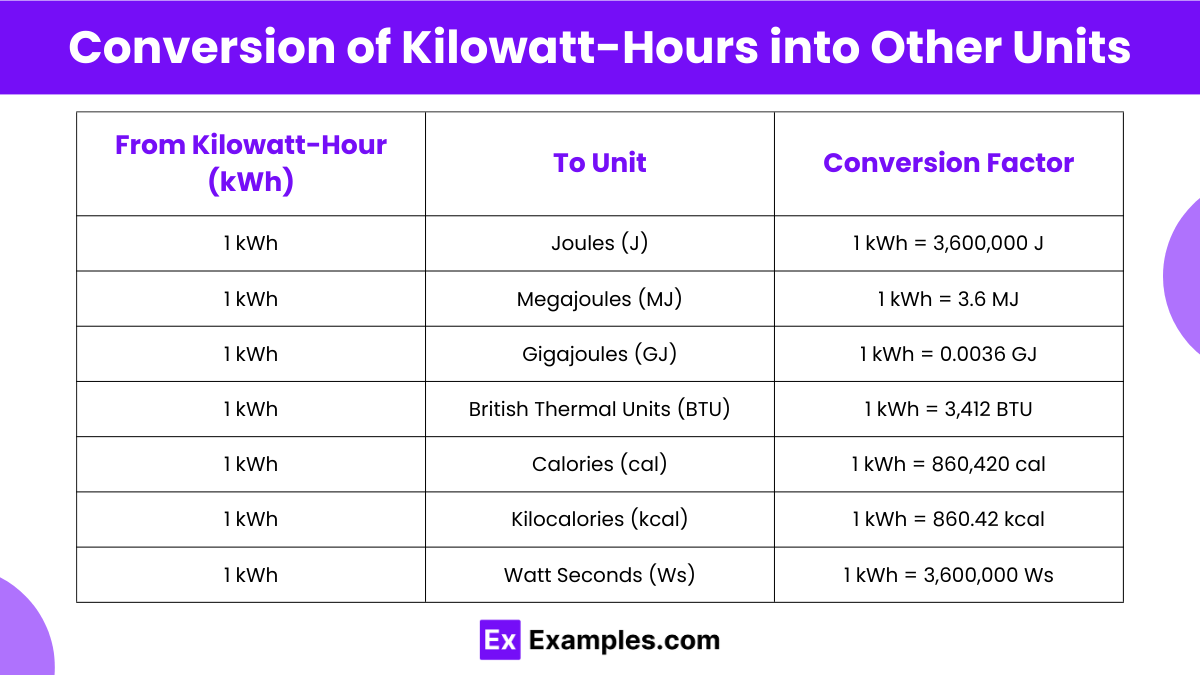
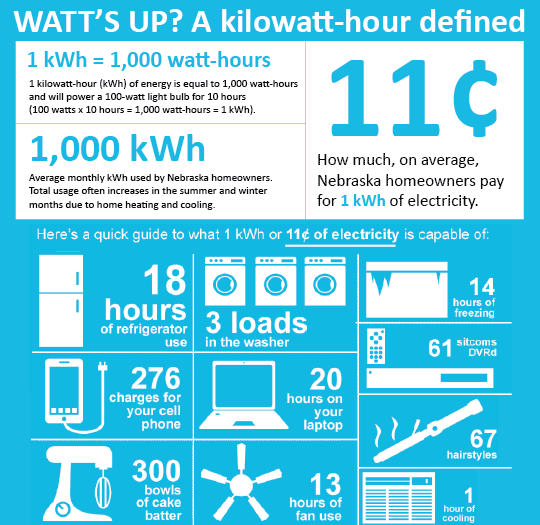
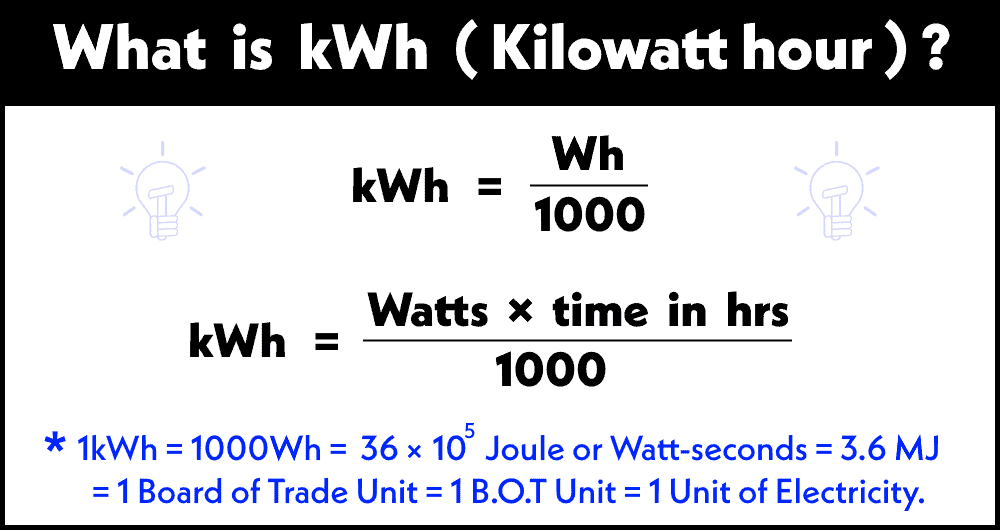
Here's the breakdown: One kilowatt (kW) equals 1000 watts. A kilowatt-hour (kWh) means you've used 1000 watts of power for one hour. For example, if you have a 100-watt light bulb and you leave it on for 10 hours, you've used 1000 watt-hours, or 1 kWh. Simple, right?
Why should you care? Different people benefit in different ways:
For Beginners: Understanding kWh helps you become more aware of your energy footprint. Knowing that your old TV uses a lot more watts than your new LED one can motivate you to make energy-efficient choices.
For Families: Keep track of your family's energy use and identify areas to cut back. This is especially helpful for managing costs with big families and bigger appliances. Consider the big ones: refrigerators, AC units, and clothes dryers. Small changes can add up to big savings!
For Hobbyists (like gamers or makers): Calculating the energy consumption of your gaming rig or workshop tools allows you to budget for your hobby and potentially explore renewable energy sources to power them.
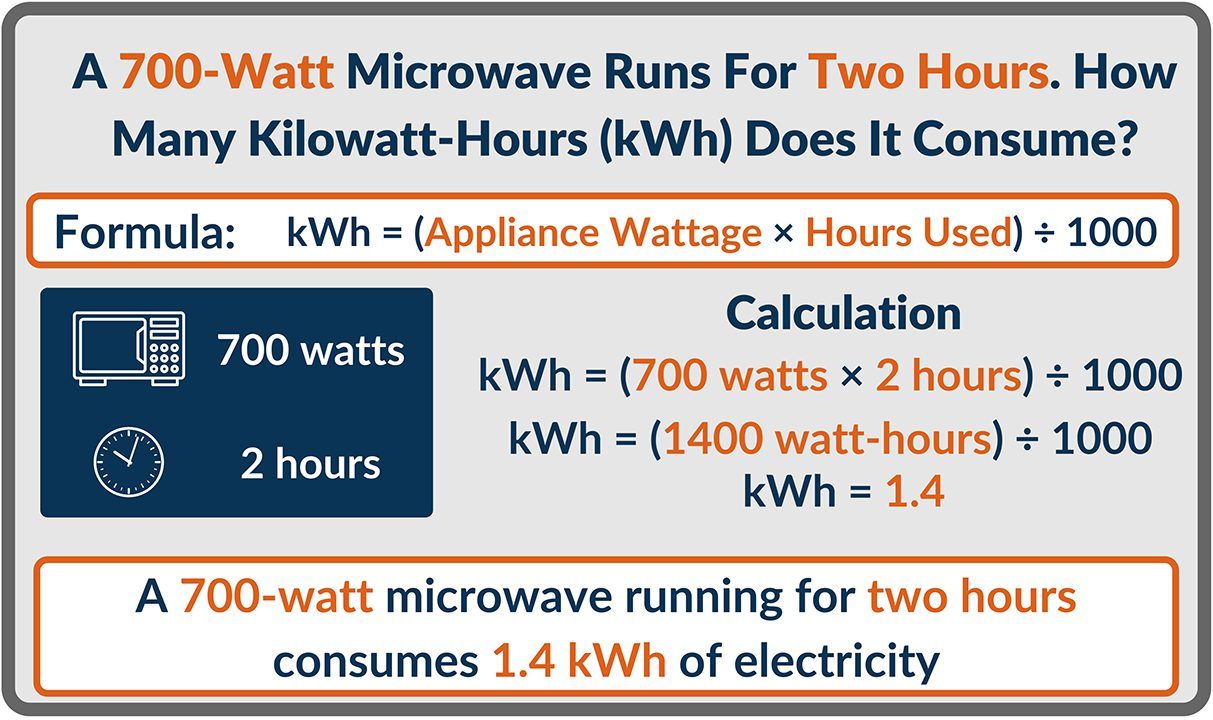
Examples and Variations: Consider a few common appliances: A microwave might use 1000 watts (1kW) when it's running, meaning it uses 1 kWh in an hour. A refrigerator, on the other hand, uses less power on average but runs much longer, so it could easily consume several kWh per day. Electric vehicle (EV) charging is another great example. Knowing the kWh capacity of your car's battery and the wattage of your charger helps you estimate charging times.
Getting Started: The easiest way to track your energy usage is to monitor your electricity bill. It usually shows your kWh consumption for the month. You can also use energy monitoring devices or smart plugs that track the wattage and kWh usage of individual appliances. Simply Google the wattage of your appliances - that info is usually readily available. Use that figure to estimate the usage of each appliance.
Here are some practical tips:
- Switch to LED lighting. They use significantly fewer watts than incandescent bulbs.
- Unplug devices when not in use. Many electronics continue to draw power even when turned off (this is known as "phantom load").
- Use energy-efficient appliances. Look for the Energy Star label when buying new appliances.
Understanding the difference between watts and kilowatt-hours opens a door to informed energy consumption. It’s not just about saving money; it’s about making conscious choices that benefit the environment. With a little knowledge and effort, you can transform from an energy consumer into an energy master, making your home more efficient and your wallet a little bit happier.