Ever wonder what makes up, well, everything? It all boils down to tiny particles called atoms, and nestled within those atoms are even tinier particles called neutrons. Understanding neutrons isn't just for scientists in lab coats; it's a peek into the fundamental building blocks of our universe! And today, we're focusing on a particularly interesting element: tungsten.
So, why tungsten? Tungsten is that incredibly strong and durable metal you might encounter without even realizing it. It's the stuff that makes the filaments in incandescent light bulbs glow, it's used in heavy machinery, and it even shows up in some jewelry. Because tungsten is so useful, it's interesting to understand what gives it those properties. That understanding begins with understanding its neutrons!
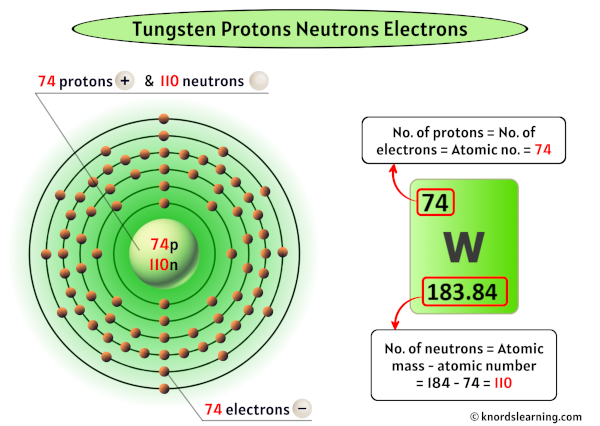
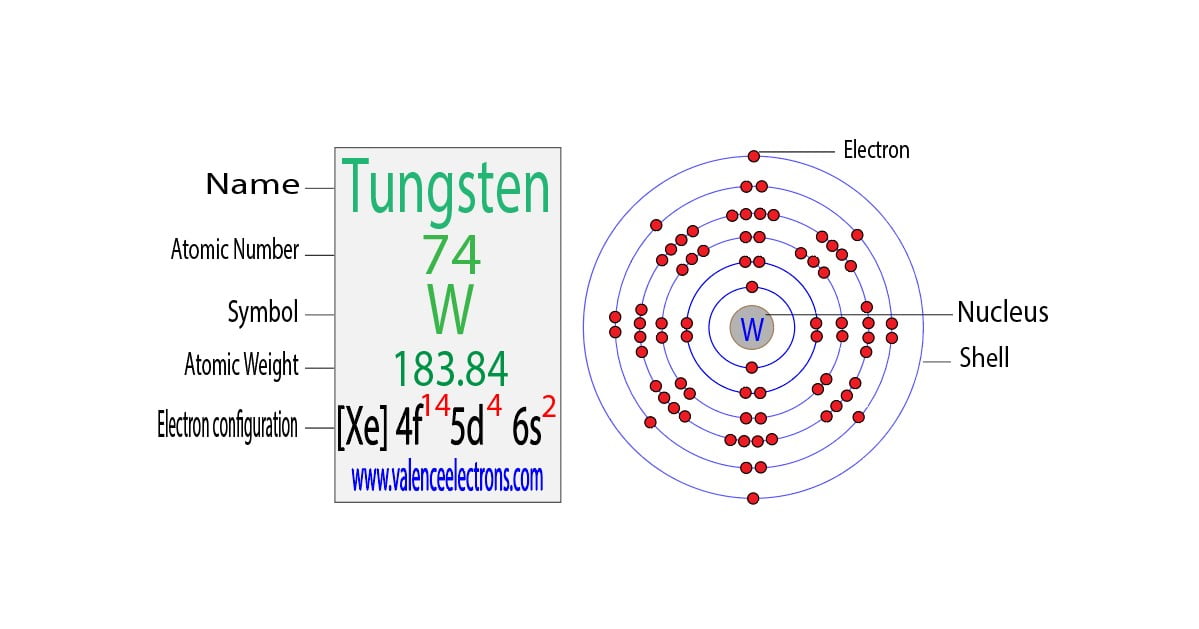
Before we dive into the neutron count, let's quickly recap what neutrons *are*. They're subatomic particles found in the nucleus (the core) of an atom, alongside protons. Unlike protons, which have a positive charge, neutrons are electrically neutral (hence the name!). The number of protons defines what element an atom is – for example, all atoms with 74 protons are tungsten. However, the number of neutrons can vary, creating different isotopes of the same element.
Now for the big question: how many neutrons does tungsten have? Well, it's not a single, fixed number. Tungsten, like many elements, exists in different isotopic forms. The most common and stable isotope of tungsten is Tungsten-184 (184W). The number 184 represents the mass number, which is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Since tungsten always has 74 protons, we can easily calculate the number of neutrons: 184 (mass number) - 74 (number of protons) = 110 neutrons.
But wait, there's more! Tungsten also exists as other isotopes, such as Tungsten-182, Tungsten-183, Tungsten-186, and so on. Each of these isotopes will have a different number of neutrons. For example, Tungsten-182 would have 182 - 74 = 108 neutrons.
Why is all this important? Understanding isotopes and neutron numbers helps us in various fields. In medicine, radioactive isotopes are used for diagnosis and treatment. In geology, isotopes help us date rocks and understand the Earth's history. Even in archaeology, isotope analysis can reveal the origins of ancient artifacts. Understanding the fundamentals, like the number of neutrons in an atom, underpins all these applications.
So, how can you explore this further? A simple way is to look up the periodic table and choose an element. Find its atomic number (the number of protons) and then search for the common isotopes of that element. Subtract the atomic number from the mass number of each isotope to find the number of neutrons. You can also find lots of interactive resources and simulations online that let you build atoms and explore their properties. Dive in and have fun exploring the microscopic world!