Hey there, tech buddy! Ever wondered how much juice your computer's actually sucking down? You're not alone! It's a question that pops up more often than you think, especially when you're trying to figure out if you can plug your hair dryer into the same outlet (spoiler alert: maybe don't!). So, let's dive into the world of computer amps, without getting too bogged down in complicated electrical engineering jargon, shall we?
First things first: what are amps? Think of them like the water flow in a pipe. Voltage is the pressure pushing that water, and watts are the total amount of "work" the water's doing. Amps are simply the rate at which the electricity is flowing. And in our case, we want to know how much 'electrical water' our computer is guzzling.
So, How Many Amps Are We Talking?
Okay, the big question! The truth is, it's not a one-size-fits-all answer. It depends heavily on what kind of computer you're rocking. A tiny little Chromebook? Probably not much. A beastly gaming rig with more RGB than a disco ball? Well, buckle up.
Here's a general breakdown:
- Laptop: A typical laptop might draw somewhere between 0.5 to 2 amps. Think of it like a tiny hummingbird sipping nectar. Pretty efficient, right?
- Desktop (Basic): A basic desktop, used for browsing the web and writing emails, might pull around 1 to 3 amps. Still relatively modest.
- Gaming PC: Now we're talking! A gaming PC with a powerful graphics card and all the bells and whistles could easily draw 5 amps or even more, especially when you're pushing it to its limits with the latest AAA title. Imagine a thirsty hippopotamus at a watering hole.
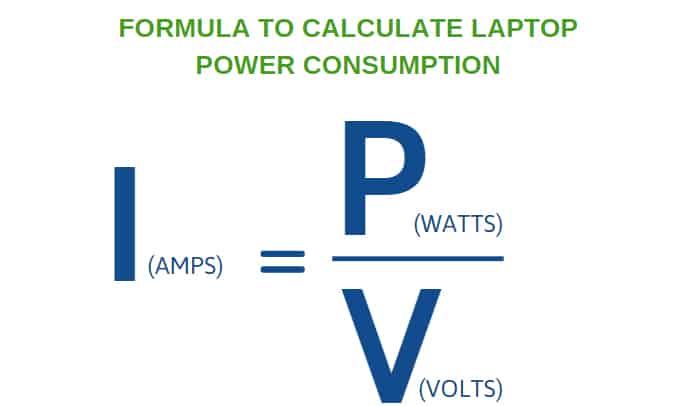
Important Note: These are just estimates. The best way to know for sure is to look at the power supply unit (PSU) inside your computer. It will list its wattage. To calculate the amps, you can use the formula: Amps = Watts / Volts. In most countries, the voltage is around 120V (in the US) or 230V (in Europe). So, if your PSU is 600W and your voltage is 120V, then your computer *could* theoretically draw up to 5 amps (600/120 = 5). But remember, it won't always be drawing that much.
Factors That Affect Amp Draw
Okay, so we know it varies, but why does it vary? Here are a few key culprits:
- Components: The beefier your graphics card, processor, and other components, the more power they'll need. Think of it like comparing a scooter to a monster truck.
- Usage: Are you just browsing the internet, or are you rendering a 4K video? The more you're asking your computer to do, the more amps it will draw.
- Age: Older computers might be less efficient and draw more power than newer models. It's like comparing a vintage car to a modern hybrid.
Why Should You Even Care?
Good question! Knowing your computer's amp draw is useful for a few reasons:
- Circuit Overload: You don't want to overload a circuit and trip a breaker. Imagine trying to pour too much water through a small pipe – it's gonna overflow!
- Power Strips: Make sure your power strip can handle the total amp draw of everything plugged into it.
- UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply): If you want your computer to stay on during a power outage, you need a UPS that can handle its power requirements.
Pro Tip: It's always a good idea to have a little extra headroom when calculating your power needs. Don't push things right to the limit. Give yourself a buffer, just in case!
Don't Panic!
Honestly, for most people, this isn't something to stress about. Unless you're running a super-powered gaming rig or have a really old electrical system, you're probably fine. But it's always good to be informed, right?
In conclusion, figuring out how many amps your computer draws is like a fun little detective game. Check your PSU, do a little math (or use an online calculator!), and you'll be an expert in no time. And remember, knowledge is power! Now go forth and conquer the world... or at least your next gaming session! You got this!