Ever flick on a light switch and wonder what's really going on? It's not magic, though it might seem that way. It's all about electrons, and they're putting on a tiny, electric show just for you. Let's unplug from the complexities and delve into the delightfully simple world of electron flow in a circuit.
Imagine a circuit as a super cool, electric racetrack. Now, picture electrons as the speedy little race cars. These aren't your grandpa's gas-guzzlers; they're tiny, negatively charged particles zooming around, delivering power wherever it's needed. The starting line? A power source – your battery or wall outlet. The finish line? Your lightbulb, your phone charger, or any device that craves electricity.
The Electron Flow Lowdown: Drifting with a Purpose
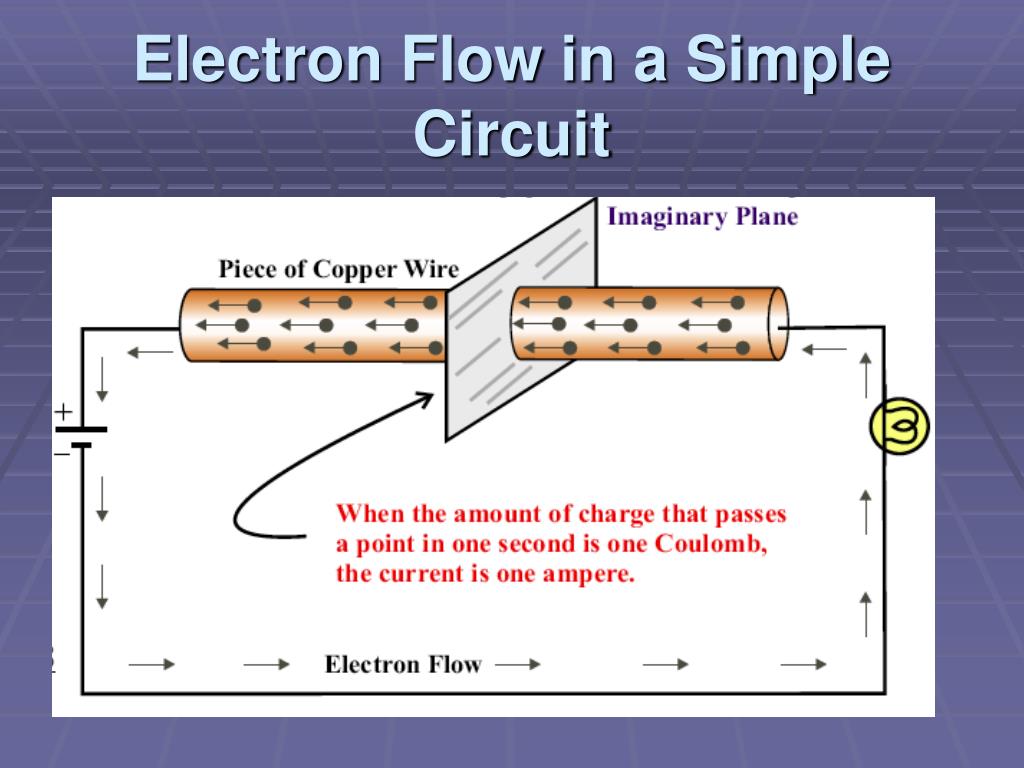
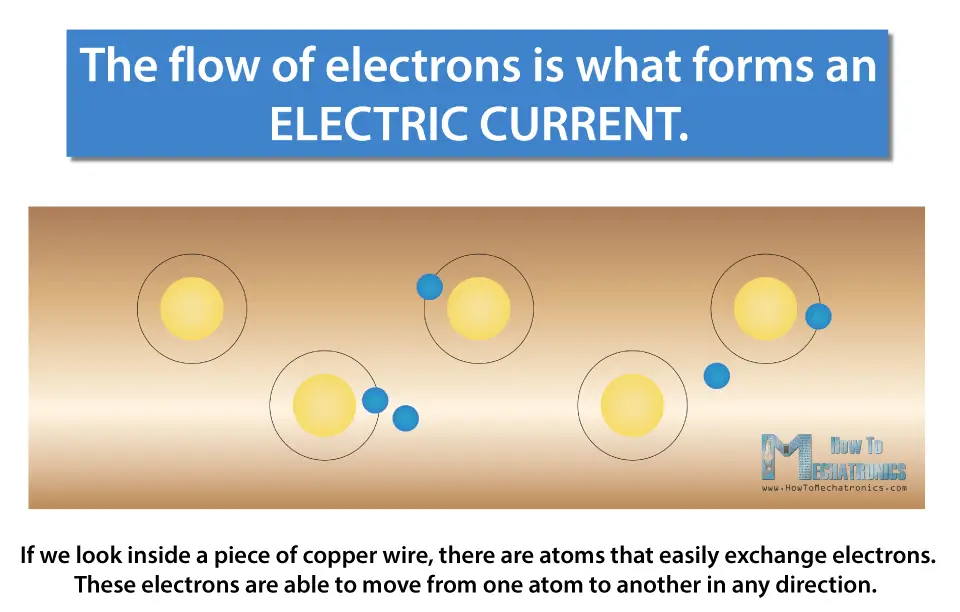
Here's the thing: electrons don't exactly sprint around the circuit. They're more like drifting champions, bumping and jostling their way forward. This slow, deliberate movement is called electron drift. Think of it like trying to walk through a crowded concert – you're not going to break any speed records, but you're definitely making progress toward the stage. And that stage in this case is your phone charging.
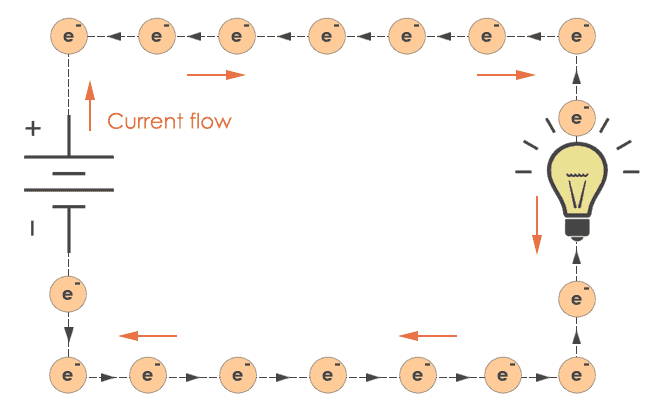
There are two main ways to think about electron flow – conventional current and electron flow. It can be confusing because they are opposite to each other.
Conventional Current: This is the old-school way of thinking, invented before we knew about electrons. It assumes current flows from positive (+) to negative (-). It's like assuming everyone drives on the left side of the road because that's what they used to do!
Electron Flow: This is the actual direction electrons move. Since electrons are negatively charged, they're attracted to the positive (+) terminal of the power source and repelled by the negative (-). So, they flow from negative (-) to positive (+).
Which one should you use? Most textbooks and engineers still stick with conventional current, but understanding electron flow is key to grasping the fundamental physics. Think of it like understanding the backstory to your favorite superhero – it adds depth!
Components in the Circuit: The Supporting Cast
Our electric racetrack isn't just a loop of wire. It has supporting players, each with a crucial role:
- Voltage: This is the force that pushes the electrons around the circuit. Think of it as the engine of our race car. More voltage? More oomph!
- Current: This is the rate of electron flow. It's like the number of cars zooming past a certain point on the track per second. Measured in Amps, this is the real workhorse of the circuit.
- Resistance: This opposes the flow of electrons. Think of it as a speed bump. A resistor controls how much current flows through the circuit.
Ohm's Law (V = IR) elegantly relates these three. It's the electric equivalent of E=mc², a fundamental equation that governs a huge part of our modern world.
Practical Tips and Everyday Examples
So, how does all this electron flow knowledge translate into real life?
- Battery Life: Devices with higher current demands drain batteries faster. Understanding electron flow helps you appreciate why your phone battery poops out quicker when you're playing a graphics-intensive game.
- Extension Cords: Overloading an extension cord can cause it to overheat. Too much current trying to squeeze through a wire that's too thin creates resistance, generating heat. This is why you should never plug a space heater and a hair dryer into the same extension cord!
- Safety First: Never mess with electrical wiring unless you know what you're doing! Electricity is powerful and can be dangerous. It's always better to call a professional.
Fun Fact!
Did you know that the speed of electricity (the speed at which the electric field propagates) is close to the speed of light, while the actual drift velocity of the electrons is incredibly slow, often just millimeters per second? It's like a wave in a stadium: the wave travels quickly around the stadium, but each individual person only moves up and down a little bit.
Another fun fact! Copper is used in most wires because it's a *very* good conductor of electricity, meaning it allows electrons to flow easily.
Reflection: The Invisible World Around Us
Electron flow might seem like a complex topic best left to physicists, but understanding the basics can give you a newfound appreciation for the technology that surrounds us. Every time you turn on a light, use your phone, or start your car, you're harnessing the power of these tiny particles in motion. It's a reminder that there's a whole world of intricate and fascinating physics humming beneath the surface of our everyday lives, silently powering our modern existence. So, next time you flip a switch, take a moment to appreciate the electron party happening behind the scenes!