Ever wondered about the magic point where a solid turns into a liquid? Let's talk about tin! It's a cool metal, and we're going to explore when it decides to melt.
The Big Reveal: Tin's Melting Point
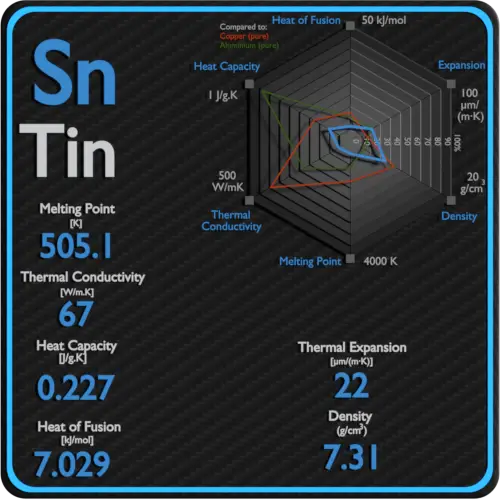
Okay, drumroll please... Tin melts at a temperature of 232 degrees Celsius. That's about 450 degrees Fahrenheit. Pretty hot, but not as scorching as some other metals!
Think of it like this: you could bake a cake at that temperature. But instead of cake, you'd get a puddle of shiny, molten tin.
Why Should You Care About Tin's Melting Point?
Why is this temperature so fascinating? Well, lots of reasons! It's not just a random number. It's a key to understanding how tin behaves.
Knowing this helps us use tin in all sorts of cool ways. From electronics to food packaging, the melting point is crucial.
Tin in Action: Where You'll Find It
Tin isn't just some obscure element in a chemistry textbook. It's everywhere! You probably use things containing tin every single day.
One of the most common uses is in solder. Solder is that melty stuff used to connect wires and electronic components.
Ever wondered how your gadgets stay connected inside? Thank tin! It's the glue that holds the electronic world together.
Tin is also used in plating other metals, like steel. This protects them from corrosion and rust.
And, believe it or not, it's in some food cans too! Although other materials are becoming more common, tin linings were a staple for preserving food for ages.
A Little Experiment (Don't Try This at Home!)
Imagine you had a chunk of pure tin. And you had a super-precise thermometer.
As you heat the tin, the temperature rises. At 232°C (450°F), something amazing happens. The tin starts to transform!
It slowly transitions from a solid, silvery metal to a shimmering, liquid pool. It's a physical change you can witness firsthand.
Of course, messing around with molten metal is dangerous! So, let's leave the actual melting to the professionals.
Comparing Tin to Other Metals
So, how does tin's melting point stack up against other metals? It's actually quite low compared to many.
Iron, for instance, melts at a whopping 1538°C (2800°F)! That's way hotter than what you need to melt tin.
Lead, another metal you might have heard of, melts at 327°C (621°F). A bit higher than tin, but still relatively low.
This relatively low melting point is one reason why tin is so useful. It's easy to work with at lower temperatures.
The Science Behind the Melting
Okay, let's get a tiny bit scientific. What's actually happening when tin melts?
It's all about the atoms! In solid tin, the atoms are arranged in a tightly packed structure.
When you heat it up, you're giving those atoms energy. They start to vibrate more and more.
At 232°C (450°F), they have enough energy to break free from their rigid structure. The solid becomes a liquid.
Fun Facts About Tin
Did you know that tin used to be much more valuable? Back in the Bronze Age, it was a key ingredient in making bronze.
Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin. It was used to make tools, weapons, and all sorts of things.
Tin's symbol on the periodic table is Sn. This comes from the Latin word "stannum," which means tin.
And here's a weird one: tin pest! At very cold temperatures, tin can actually crumble into a gray powder. It's a rare but fascinating phenomenon.
Why is Melting Point Important in General?
It's not just about tin. Melting points are important for all kinds of materials. They help us understand how things behave under different conditions.
Engineers use melting points to design everything from bridges to airplanes. Chefs use them to cook delicious food.
Knowing when something will melt can prevent disasters and create amazing innovations. It's a fundamental property of matter.
Tin Alloys: Mixing Things Up
Pure tin is great, but sometimes it's even better when mixed with other metals. These mixtures are called alloys.
Bronze, as we mentioned earlier, is a classic example. But there are many other tin alloys out there.
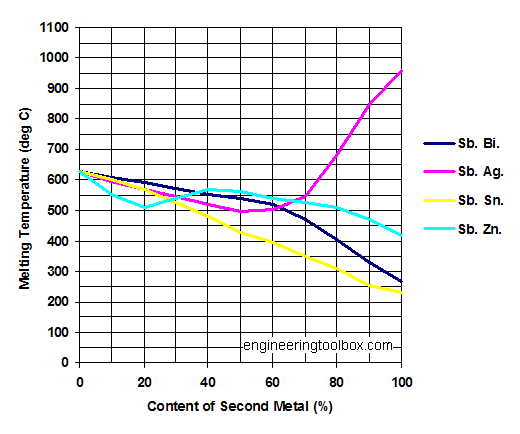
Pewter is another one. It's an alloy of tin with smaller amounts of other metals like antimony and copper.
These alloys often have different melting points and properties than pure tin. This allows us to tailor them for specific applications.
Tin and the Environment
Mining tin, like any mining activity, can have environmental impacts. It's important to extract tin responsibly.
Recycling tin is also crucial. It helps conserve resources and reduce pollution.
By being mindful of where our tin comes from and how it's used, we can help ensure a more sustainable future.
Back to That Melting Point...
So, remember, tin melts at 232°C (450°F). It's a key piece of information that unlocks a world of possibilities.
From soldering electronics to preserving food, tin's melting point plays a vital role in our modern lives.
The next time you see something made of tin, remember the science behind it. Think about those atoms vibrating and breaking free!
Explore Further!
Hopefully, this has sparked your curiosity about tin and melting points. There's so much more to learn!
Dive into the world of metallurgy. Explore the properties of other metals. Conduct (safe!) experiments.
Science is all around us. And understanding the melting point of tin is just the beginning of a fascinating journey.
So, go forth and discover! The world of materials science awaits.
And remember, 232°C (450°F) is the magic number for tin!
You can even remember tin melting point as an important information that would help you do more research.