Ever seen a mesmerizing spark shower while someone's welding? Or perhaps you've admired a perfectly smooth weld bead, wondering what secrets lie behind it? While welding seems like an intimidating craft, understanding some of the underlying principles can be surprisingly engaging. Let's dive into one aspect that plays a crucial role in creating strong and clean welds: argon gas setting for MIG welding. It’s more than just turning a knob; it's about controlling the very environment where metal joins.
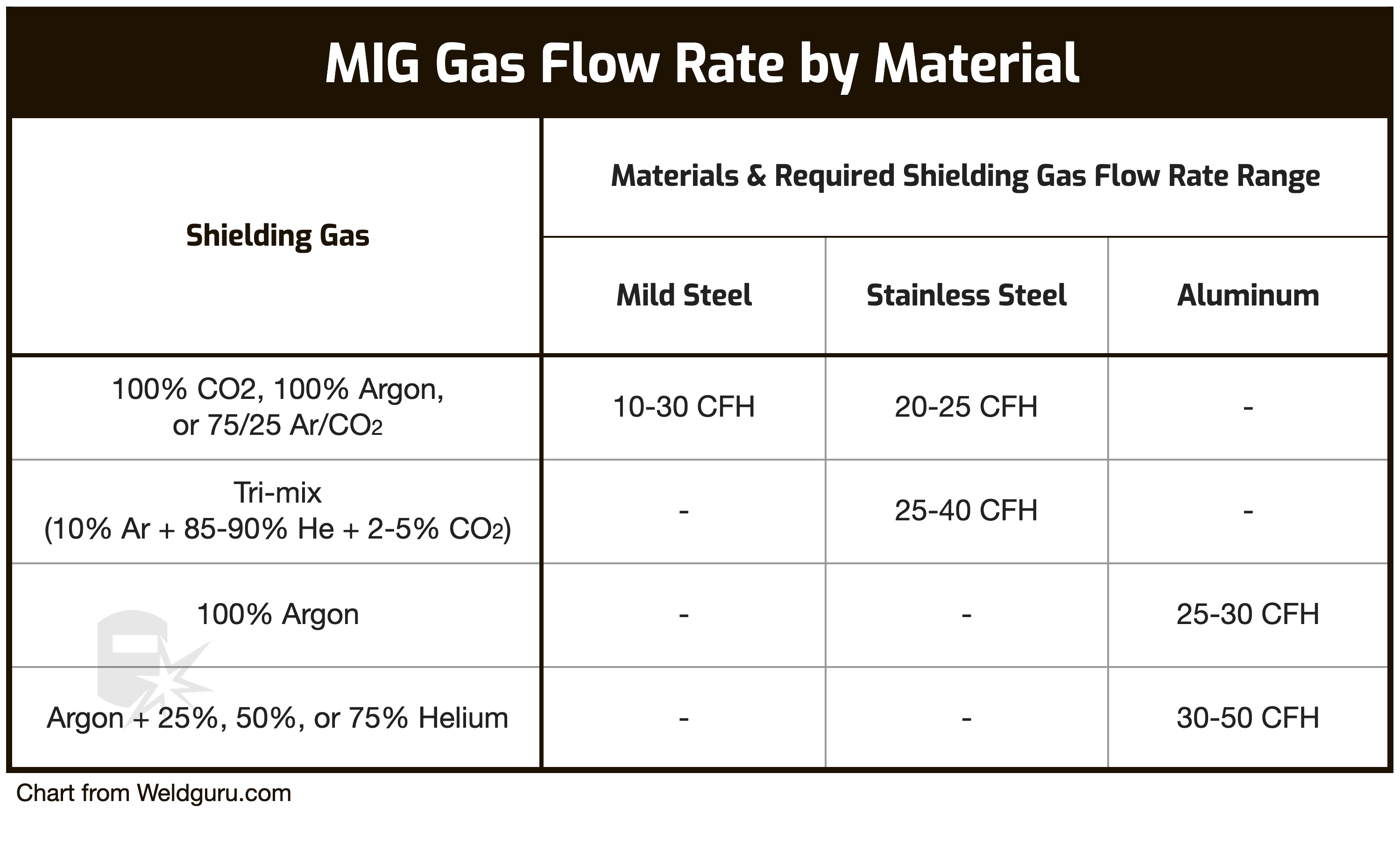
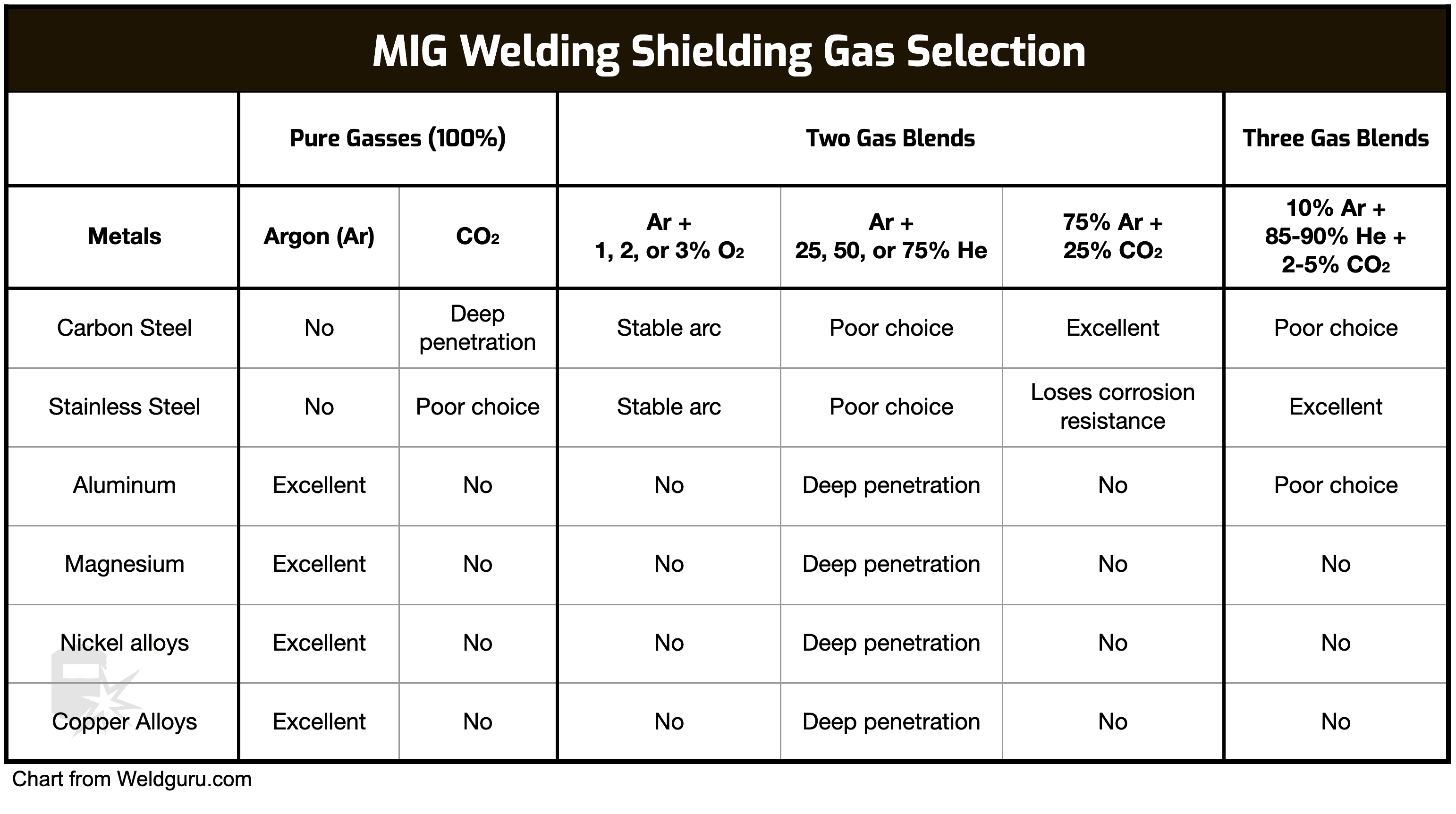
So, what's the big deal with argon? In MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, also known as GMAW (Gas Metal Arc Welding), we're melting metal to fuse pieces together. But molten metal is incredibly reactive with the air around it. Oxygen and nitrogen in the air can contaminate the weld, leading to porosity (tiny holes), brittleness, and a generally weak joint. That’s where argon steps in as a silent guardian. Its primary purpose is to create an inert shield around the weld pool, preventing atmospheric gases from interfering with the molten metal. Think of it like a personal force field for your weld!
The benefits are significant. Using argon provides a cleaner, stronger, and more ductile weld. It helps produce welds with better aesthetics, meaning they look nicer too. Argon also helps stabilize the arc, making the welding process smoother and easier to control, which is especially helpful for beginners. In essence, argon makes the welding process more predictable and reliable.
You might be surprised where MIG welding, and therefore argon, pops up in everyday life. Think about the frames of your cars and bicycles; those are often MIG welded. In the classroom, students learning metal fabrication rely on proper argon settings to create projects ranging from simple brackets to complex sculptures. DIY enthusiasts building metal furniture or repairing equipment also use MIG welding with argon shielding gas. It’s the invisible ingredient that helps create robust and durable structures all around us.
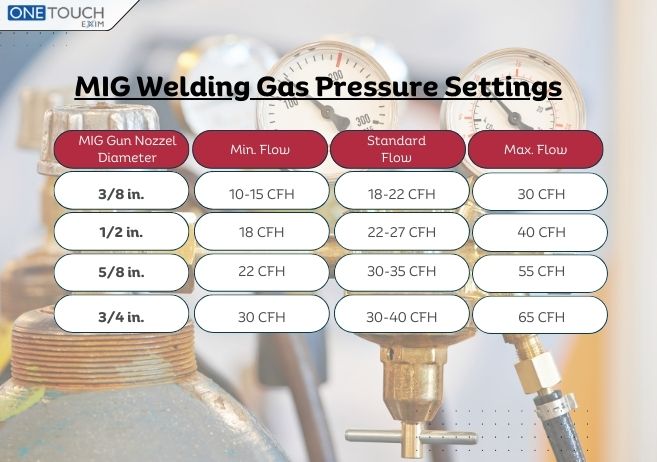
Want to explore the world of argon and MIG welding a bit further? Here are a few practical tips: First, start by observing. If you know someone who welds, ask if you can watch them work and ask questions about their gas settings. You can even find countless videos online demonstrating different argon flow rates and their effects on the weld. Secondly, consider taking a basic welding course. Many community colleges and vocational schools offer introductory courses where you can learn the fundamentals of MIG welding and the importance of argon settings under the guidance of experienced instructors. Finally, experiment (safely!). If you have access to a MIG welder, try varying the argon flow rate and observing the resulting weld. Always wear proper safety gear, including a welding helmet, gloves, and protective clothing. Start with scrap metal and practice adjusting the settings to find what works best for different materials and thicknesses. Remember to consult your welder’s manual for specific recommendations.
Understanding argon gas settings might seem like a niche topic, but it’s a critical piece of the puzzle when it comes to producing high-quality MIG welds. So next time you see someone welding, you'll have a better appreciation for the invisible gas working behind the scenes to create a strong and lasting bond.